Error P0507 - Idle Speed Control System
Determining the P0507 Error Code
Trouble P0507 is a general trouble code that indicates there is a problem with the idle speed control system. P0505 and P0506 may also appear along with this code .
What does P0507 mean?
Trouble code P0507 indicates that the idle speed is too high. The ECU is set to a certain idle speed range, and if the speed is higher than the permissible values, the P0507 code appears. When this error occurs, the vehicle will enter Safe Mode and the Check Engine light will illuminate on the dashboard.
Causes of error P0507
- Intake air leak
- Clogged or faulty idle air valve
- Carbon buildup on the throttle body
- Power steering oil pressure switch malfunction
- Alternator fault
What are the symptoms of a P0507 code?
- Check Engine Light Illuminates
- High engine speed at idle
- Unstable idle
- Problems starting a car engine
- Rough idle
How does a mechanic diagnose a P0507 trouble code?
When diagnosing this error code, a mechanic will do the following:
- Reads all stored error codes using an OBD-II scanner.
- Review all saved data and clear error codes.
- Will test drive the car to make sure there is a problem.
- Check the vacuum wires for damage and also check for intake air leaks.
- Check the throttle body for large amounts of carbon buildup and the throttle body for proper opening and closing.
- Determines the engine idle speed when checking the idle air control valve and oil pressure switch in the power steering system using a diagnostic tool.
- Check the battery charging system.
Common errors when diagnosing code P0507
The most common mistake when diagnosing this code is failure to follow the diagnostic procedure, which leads to the erroneous replacement of serviceable parts.
How serious is the P0507 code?
When a P0507 code appears, rough idling may occur and may affect vehicle performance, but in most cases the engine will not stall.
What repairs can fix the P0507 code?
- Cleaning or replacing the idle air control valve
- Repairing Intake Air Leaks
- Repair of battery charging system
- Cleaning the Throttle Body
- Replacing the Power Steering Oil Pressure Switch
Additional comments for troubleshooting P0507
Over time, large amounts of carbon can accumulate on the throttle body and idle air control valve (usually if the vehicle has been driven more than 140,000 kilometers). Carbon buildup can cause these parts to become clogged and not function properly. A throttle body cleaner can be used to remove carbon deposits.
Need help with error code P0507?
The company - CarChek, offers a service - on-site computer diagnostics; specialists from our company will come to your home or office to diagnose and identify problems with your car. Find out the cost and sign up for a comprehensive car diagnostic or contact a consultant by phone
How does a mechanic diagnose a P0507 trouble code?
When diagnosing this error code, a mechanic will do the following:
- Reads all stored error codes using an OBD-II scanner.
- Review all saved data and clear error codes.
- Will test drive the car to make sure there is a problem.
- Check the vacuum wires for damage and also check for intake air leaks.
- Check the throttle body for large amounts of carbon buildup and the throttle body for proper opening and closing.
- Determines the engine idle speed when checking the idle air control valve and oil pressure switch in the power steering system using a diagnostic tool.
- Check the battery charging system.
Description and meaning of error P0507
This diagnostic trouble code (DTC) is a generic powertrain code, which means it applies to OBD-II equipped vehicles. While general, specific repair steps may vary depending on the make/model. Acedotally this code seems to be more common on Chevrolet, VW, Nissan, Audi, Hyundai, Honda, Mazda and Jeep vehicles. This P0507 code is one that sometimes triggers on vehicles that have electronic throttle control. That is, they don't have a conventional throttle cable from the accelerator pedal to the engine. They rely on sensors and electronics to control the throttle. In this case, a p0507 DTC (diagnostic trouble code) is triggered when the PCM (powertrain control module) detects an engine idle speed that is greater than the desired (programmed) RPM. In the case of GM (and other) vehicles, if the idle speed is greater than 200 rpm higher than expected, this code will be set.
What does code P0507 mean?
Trouble code P0507 is triggered when the engine idle speed is higher than expected. All modern engines have a desired idle speed - usually between 600-1000 rpm.
The control unit uses position sensing and throttle adjustment to achieve these speeds. If the idle speed exceeds these set values and the maximum adjustment zone, the control unit will generate this error code.
Code P0507 is a common code for vehicles equipped with Electronic Throttle (E-Gas). Newer vehicles usually use E-gas.
The throttle valve is only called electronic. It replaces the old throttle body with a cable between the gas pedal and the throttle body.
The electronic throttle body uses sensors on the gas pedal and an electric motor in the throttle body to provide the desired acceleration. But this does not mean that this error code must necessarily be related to a faulty throttle valve. It can also have many other causes.
VAZ P0507 High idle speed
Code P0507 is entered if:
there are no fault codes P0102, P010З, P0115, P0117, P0118, P0122, P0123, P0444, P0445, P1509, P1513, P1514; the engine is idling; coolant temperature above 84°C; within 3 seconds, the crankshaft speed of the N10 engine is less than 900 rpm; within 3 seconds, the current correction of the calculated idle air flow IV exceeds 10 kg/h.
If a permanent malfunction occurs, the “CHECK ENGINE” lamp lights up after 2 drive cycles.
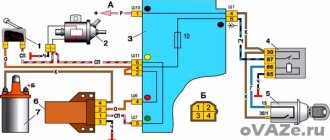
The idle speed control is checked using the TDRKH-1 tester (Samara) or J-34730-3 (from UTS. USA).
HOW TO CHECK:
Connect the adapter cable to the diagnostic connector. Start the engine and warm it up to a coolant temperature of 84°C. Using the Errors menu, check whether the fault code is currently active.
Code P0507 is intermittent. If it is currently inactive and there are no other codes, analyze the conditions under which the code occurred.
High idle speed may be caused by a problem that cannot be overcome by the idle speed control. To troubleshoot problems not related to the idle air control, the following checks must be performed.
Over-lean mixture. The idle speed may be low or unstable. Check the fuel supply system for low fuel pressure, water in the fuel or dirty injectors. Check the oxygen sensor for contamination with silicone, glycol or other materials.
Crankcase ventilation system. A malfunction of the crankcase ventilation system can lead to deviations in idle speed. See Map C-7.
Check the system for air leaks. If a malfunction is detected, correct it.
1. Disconnect the harness connector from the regulator. Connect the idle air control tester wires to the battery, then connect its connector to the idle air control control. Start the engine.
Using the tester, control the regulator by setting the idle speed to decrease.
If the idle speed decreases, replace the controller. If they do not decrease, replace the idle speed control.
After repair, start the engine, reset the codes and make sure there is no signal from the “CHECK ENGINE” lamp.
Possible causes of error P0507
Wiring, idle speed control actuator/idle air control valve, throttle actuator motor, throttle sticking, ECM
The P0507 DTC trouble code can be caused by one or more of the following: vacuum leak Leaking air intake after throttle bodyegr valve Leaking vacuuma faulty positive crankcase ventilation (PCV) valveDamaged/failing/dirty throttle bodyFailed evap systemFailed IAC (inoperative air regulator) or faulty circuit IAC
Fault code P0507
624 Google+ If, when the engine is running warm (coolant temperature is at least 84 degrees C) in idling mode for three seconds, the engine crankshaft revolutions are above 900 rpm and at the same time the current correction of the calculated air flow is below -10 kg/h , fault code P0507 (low idle speed) is entered into the controller's RAM.
In this case, the controller memory must not contain fault codes P0102, P0103, P0115, P0117, P0118, P0122, P0123, P0444, P0445, P1509, P1513, P1514. If the fault persists for two drive cycles, the Check Engine light will illuminate on the instrument panel.
Fault code P0507 check.
Checking the operation of the idle speed control can only be done using diagnostic equipment. You can also use a personal computer connected to the diagnostic line of the controller using an adapter. Fault code P0507 may also appear when the mixture is too lean. To detect and eliminate the malfunction, it is necessary to check the fuel supply system for low pressure and the presence of water in the fuel. Check the oxygen sensor for contamination with silicone or other substances. Check the injectors for contamination. It is also possible that foreign air may leak from under the intake manifold gasket, vacuum brake booster or air pipes, after the mass air flow sensor. In addition, unstable engine operation may be caused by a malfunction of the crankcase ventilation system.
admin 03/11/2011 “If you notice an error in the text, please highlight this place with the mouse and press CTRL+ENTER” “If the article was useful to you, share the link to it on social networks”
error 0507 on VAZ 2114
error 0507 for VAZ 2114 If, when the engine is running warm (coolant temperature is at least 84 degrees C) in idle mode for three seconds, the engine crankshaft speed is above 900 rpm and at the same time the current correction of the calculated air flow is below -10 kg/hour, fault code P0507 (low idle speed) is entered into the controller’s RAM memory. In this case, the controller memory must not contain fault codes P0102, P0103, P0115, P0117, P0118, P0122, P0123, P0444, P0445, P1509, P1513, P1514. If the fault persists within two drive cycles, the Check Engine light will illuminate on the instrument panel.
Checking the operation of the idle air control regulator can only be carried out using diagnostic equipment or a personal computer connected to the diagnostic line of the controller using an adapter. The appearance of fault code P0507 is also possible when the mixture is too lean. To detect and eliminate the malfunction, it is necessary to check the fuel supply system for low pressure and the presence of water in the fuel. Check the oxygen sensor for contamination with silicone or other substances. Check the injectors for contamination. It is also possible that foreign air may leak from under the intake manifold gasket, vacuum brake booster or air pipes, after the mass air flow sensor.
In addition, unstable engine operation may be caused by a malfunction of the crankcase ventilation system. .
How is self-diagnosis performed?
We have sorted out the main errors on the Priora, now it’s worth finding out how self-diagnosis is performed. The VAZ 2170 with 16 valves has a special controller with which diagnostics are performed. If you have an on-board computer installed, then diagnostics are performed on it. There is also special equipment that allows for a more in-depth check of Priora 16 class systems.
Since most Priora 16 cars already have an on-board computer, we will consider the option without the use of special devices. Diagnostics begins with activation of the test mode. The work proceeds according to the following scheme:
- Turn off the ignition. Now we hold down the daily mileage reset button, without releasing the button, we start the ignition of the Priora 16 cl;
- On the instrument panel you will see a display with an indication. After turning on the ignition, all components of the instrument panel will light up. The needles of the temperature, speedometer, tachometer and other instruments will begin to move to the maximum level and back. This behavior indicates that self-diagnosis has begun;
- Let's move on to the right steering wheel switch. Here you will find a button for switching the on-board computer settings. Click on it, a message with the software version will appear on the instrument panel screen;
- The instrument panel error diagnosis will begin if you press this key again. Various codes will appear on the display, which you can decipher in the table below;
- When the diagnostics are complete, you can reset the error data. Press and hold the daily mileage reset button for about 5 seconds.
Error 0506 – low idle speed
The error is entered under the following conditions:
1. The engine runs at idle.
2. Coolant temperature is above 75 degrees.
3. Crankshaft speed less than 700 rpm
4. The integral part of the desired torque to maintain idle (parameter DMLLRI) has exceeded the threshold value.
The error is entered into the ECU memory on the third drive cycle.
Unstable or reduced idle speed can be caused by the following factors.
• Incorrect connection of the crankcase ventilation system hoses, presence of a large amount of dirt.
• Over-lean mixture. Check the fuel system for low fuel pressure, contamination of injectors, DC for contamination with glycol, silicone...
• Over-rich mixture. Check the fuel system for increased fuel pressure, contamination of injectors, DC for contamination with glycol, silicone...
• Contamination of the IAC rod (sticking due to contamination)
To carry out the test, a diagnostic device with the function of controlling the actuators is required.
How to resolve error P0507?
This DTC is larger than the information code, so if there is any other codesset, diagnose them first. If there are no other codes, check the air intake system for air or vacuum leaks and damage. If there are no symptoms other than the DTC itself, simply clear the code and see if it returns. If you have an advanced scan tool that can interface with the car, theidle command above and below will see if the engine responds accordingly. Also check the PCV valve to see if it is blocked and needs to be replaced. Check IAC (idle Air controller) if equipped, check its operation. If available, tryswapping in a new throttle body to see if that fixes the problem. On NissanAltimas and possibly other vehicles the problem can be corrected by having dealerperform idle air relearn procedures, or other relearn procedures.
Fault code P0506
246 Google+ If, when the engine is running warm (coolant temperature is at least 84 degrees C) in idling mode for three seconds, the engine crankshaft speed is less than 740 rpm and at the same time the current correction of the calculated air flow exceeds 10 kg/hour, DTC P0506 (low idle speed) is entered into the controller's RAM memory.
In this case, the controller memory must not contain fault codes P0102, P0103, P0115, P0117, P0118, P0122, P0123, P0444, P0445, P1509, P1513, P1514. If the fault persists for two drive cycles, the Check Engine light will illuminate on the instrument panel.
Fault code P0506 check.
Checking the operation of the idle air control regulator can only be carried out using diagnostic equipment or a personal computer connected to the diagnostic line of the controller using an adapter. The appearance of fault code P0506 is also possible when the mixture is too lean or too rich. To detect and eliminate the malfunction, it is necessary to check the fuel supply system for low or high pressure and the presence of water in the fuel. Check the oxygen sensor for contamination with silicone or other substances. Check the injectors for contamination and leaks. Remove the idle air control valve and check the machined part for foreign particles. It is also possible that foreign air may leak from under the gasket of the intake manifold, vacuum brake booster or air pipes, after the mass air flow sensor.
In addition, unstable engine operation can be caused by contamination of the air filter and crankcase ventilation system. admin 01/11/2011 “If you notice an error in the text, please highlight this place with the mouse and press CTRL+ENTER” “If the article was useful to you, share the link to it on social networks”
Priora error p0507. Decoding ECU error codes
VAZ P0507 High idle speed
Code P0507 is entered if:
there are no fault codes P0102, P010З, P0115, P0117, P0118, P0122, P0123, P0444, P0445, P1509, P1513, P1514; the engine is idling; coolant temperature above 84°C; within 3 seconds, the crankshaft speed of the N10 engine is less than 900 rpm; within 3 seconds, the current correction of the calculated idle air flow IV exceeds 10 kg/h.
If a permanent malfunction occurs, the “CHECK ENGINE” lamp lights up after 2 drive cycles.
The idle speed control is checked using the TDRKH-1 tester (Samara) or J-34730-3 (from UTS. USA).
HOW TO CHECK:
Connect the adapter cable to the diagnostic connector. Start the engine and warm it up to a coolant temperature of 84°C. Using the Errors menu, check whether the fault code is currently active.
Code P0507 is intermittent. If it is currently inactive and there are no other codes, analyze the conditions under which the code occurred.
High idle speed may be caused by a problem that cannot be overcome by the idle speed control. To troubleshoot problems not related to the idle air control, the following checks must be performed.
Over-lean mixture. The idle speed may be low or unstable. Check the fuel supply system for low fuel pressure, water in the fuel or dirty injectors. Check the oxygen sensor for contamination with silicone, glycol or other materials.
Crankcase ventilation system. A malfunction of the crankcase ventilation system can lead to deviations in idle speed. See Map C-7.
Check the system for air leaks. If a malfunction is detected, correct it.
1. Disconnect the harness connector from the regulator. Connect the idle air control tester wires to the battery, then connect its connector to the idle air control control. Start the engine.
Using the tester, control the regulator by setting the idle speed to decrease.
If the idle speed decreases, replace the controller. If they do not decrease, replace the idle speed control.
After repair, start the engine, reset the codes and make sure there is no signal from the “CHECK ENGINE” lamp.
Fault code P0507
069 Google+ If, when operating a warm engine (coolant temperature at least 84 degrees C) in idling mode for three seconds, the engine crankshaft revolutions are above 900 rpm and at the same time the current correction of the calculated air flow is below -10 kg/h , fault code P0507 (low idle speed) is entered into the controller's RAM.
In this case, the controller memory must not contain fault codes P0102, P0103, P0115, P0117, P0118, P0122, P0123, P0444, P0445, P1509, P1513, P1514. If the fault persists for two drive cycles, the Check Engine light will illuminate on the instrument panel.
Fault code P0507 check.
Checking the operation of the idle speed control can only be done using diagnostic equipment. You can also use a personal computer connected to the diagnostic line of the controller using an adapter. Fault code P0507 may also appear when the mixture is too lean. To detect and eliminate the malfunction, it is necessary to check the fuel supply system for low pressure and the presence of water in the fuel. Check the oxygen sensor for contamination with silicone or other substances. Check the injectors for contamination. It is also possible that foreign air may leak from under the intake manifold gasket, vacuum brake booster or air pipes, after the mass air flow sensor. In addition, unstable engine operation may be caused by a malfunction of the crankcase ventilation system.
“If you notice an error in the text, please highlight this place with the mouse and press CTRL+ENTER”
admin 03/11/2011 “If the article was useful to you, share a link to it on social networks”
Decoding error codes Lada Priora
Note! These encodings are also relevant for the Kalina version.
Exhaust (0000)
- 30 – break or damage to the oxygen sensor heater before the catalyst;
- 31 – same as 30 with short circuit to body ground;
- 32 – similar short circuit for on-board wiring;
- 36 – break in the wiring of the oxygen heater after the catalyst;
- 37 – wiring short to ground;
- 38 – open circuit from short circuit to BS.
Air supply failure (0101, etc.)
- 102 – open or damaged air flow sensor circuit;
- 103 – short circuit of the mass air flow sensor network;
- 112/13 – violation of the temperature indicators of the air mixture on the intake manifold;
- 115/16 - failure of antifreeze temperature sensors - the system does not cool, the main fan may not work correctly;
- 117 – open circuit of DTOZH;
- 118 – short circuit of the same sensor;
- 122/23 – violation of the throttle position sensor circuit;
- 130 – error DC 1;
- 131 – break in oxygen sensor 1;
- 132 – short circuit of DPKV 1 circuit;
- 133 – difficulty in response of the oxygen sensor (possible poor contact);
- 134 – break in the oxygen sensor line;
- 135 – failure of the heating device DK2;
- 136 – ground fault DK2;
- 137/138 – weak/high impulse of DC2;
- 140 – break in the DK2 highway;
- 141 – failure of heater DK2;
- 171/172 – excessively lean/rich air-fuel mixture.
Failure to supply fuel mixture (0200)
- 201-204 – break in the control line of injectors 1-4, respectively, characterized by engine tripping;
- 217 – internal combustion engine overheating;
- 230 – open circuit of the fuel pump control relay – the engine does not turn on or does not start;
- 263/266/269/272 – failure of the injector driver for cylinders 1-4, respectively;
- 261/267/270/264 – ground fault of injector lines from 1 to 4, respectively;
- 262/265/268/271 – short circuit at 12 V.
Ignition design violation (0300)
- 300 – no spark on all cylinders (large number of misfires);
- 301/302/303/304 – ignition interruptions in 1-4 boilers, respectively (ICE triples or doubles);
- 325 – DD break or failure;
- 327/328 – violation of knock sensor readings;
- 335/336 – violation of the DPKV operation;
- 337/338 – short circuit to ground or violation of the DPKV signal;
- 340 – DRF failure;
- 342/343 – violation of the phase distribution sensor signal;
- 346 – exceeding the tolerance of DRF indicators;
- 351-354 – the wiring of the ignition coils for cylinders 1-4 is interrupted, respectively;
- 363 – no supply of fuel and air to the cylinders.
Additional equipment control systems (0400)
- 422 – catalyst is clogged – urgent replacement or repair is required;
- 441 – violation of the adsorber purge valve;
- 443 – violation of the purge circuit;
- 444 – short circuit or break in the same network;
- 445 – also with short circuit to ground;
- 480/481 – violation of the integrity of the coolant fan wires.
Engine speed control violations (0500)
- 501/502 – incorrect reading of speed sensor indicators;
- 503 – DC is loose or short-circuited;
- 505 – malfunction of the XO regulator;
- 506 - engine idle speed is too low - when the load is removed, the engine stalls;
- 507 – the opposite value of the previous code, revolutions can also float;
- 511 – failure of the XX regulator network;
- 560/562/563 – problems with the on-board network voltage.
On-board network violations (0600)
- 601 – ROM failure;
- 603/604 – internal/external RAM malfunction;
- 607 – disorder of the detonation line;
- 615 – break in the wiring of the auxiliary starter relay;
- 616 – duplicates the previous problem with a short circuit to ground;
- 617 - the same, only with a contact for the on-board wiring;
- 627 – there is no power to the fuel pump, the wires may be interrupted;
- 628 – also with a break and a short circuit to the body;
- 629 – duplicates the previous cipher with a connection to the machine’s network;
- 645 – no power supply to the air conditioning compressor clutch relay;
- 646/7 – complements the above failure with a short circuit to the body or on-board wiring;
- 650 – the “Check Engine” lamp has burned out;
- 654 – failure in the electronic part of the tachometer;
- 685/6/7 – break in the main relay wire/with a short to the body/network;
- 691/692 – break in the main cooler control circuit/with a short to other wires.
Additional signals about the causes of the malfunction (1000)
- 102 – the DC heating resistance has disappeared;
- 115 – circuit failure of the same sensor;
- 123/124 - violation of mixture formation in the absence of load - idle is acting up;
- 127/128 – duplicates the previous signal in partial load mode – jerks, dips or jerks when pressing the gas pedal lightly;
- 135 – open circuit or short circuit of circuit DK1;
- 136/137 – violation of the formation of a combustible mixture at minimum load;
- 140 – potential difference between measured and actual load;
- 171/172 – incorrect operation of the potentiometer;
- 386 – incorrect detonation channel test result;
- 410/425/426 – short circuit to the sides or ground/break in the lines of the canister purge valve;
- 500/501/502 – open circuit with short circuit of the fuel pump for ground and 12V, respectively;
- 509 – overload of the XX regulator;
- 513/514 – short circuit of the throttle position in position XX;
- 541 – there is no power to the fuel pump or the integrity of the housing may be damaged with fuel getting inside;
- 570 – an incorrect signal from the APS design is received;
- 600 – no impulse is received from the APS; there may be a breakdown or the unit is coming off;
- 602 – 12V short circuit to the electronic engine control unit;
- 603 – problems with the firmware, can be resolved by rebooting;
- 606/616 – interruptions in the operation of the rough road sensor;
- 612 – incorrect ECU reset code – the system did not reboot;
- 617 – the rough road sensor has died or a short circuit has formed;
- 620 – critical fault in the EEPROM;
- 621 – critical RAM fault;
- 622 – failure or breakdown of the EEPROM;
- 640 – conflict in checking firmware status;
- 689 - diagnostics showed that all vehicle systems are in order - erroneous codes were displayed.
Technical description and explanation of error P0507
OBD II trouble code P0507 is defined as "Idle Air Control (IAC) speed higher than expected." Set when the powertrain control module (PCM) is unable to maintain or control engine idle speed.
In most cases, the PCM will attempt to make adjustments to various systems such as fuel timing, ignition timing, injection pulse timing, and others. Trying to maintain a given idle speed. However, when this limit is reached, the PCM will set code P0507 and turn on the warning light.
Idle speed in gasoline engines is adjusted and controlled by the idle air control valve, which is usually located on the throttle body. The valve is driven by a stepper motor, which receives commands from the PCM based on information received from various sensors located on the engine.
As long as the throttle valve remains closed, idle speed and quality are controlled by the PCM through the idle air control valve.
For example, if the engine is started in sub-zero temperatures, the PCM commands the valve to allow less air to enter the engine. This allows you to enrich the fuel-air mixture and creates conditions for regulating idle speed in cold weather.
As the engine warms up and combustion becomes easier and more complete. The PCM commands the idle air control valve to increase the amount of air entering the engine in response to changing conditions.
If the load on the engine changes, for example, when some electrical consumers are turned on or off. The PCM adapts the signal voltage to the idle air control valve. To ensure that the idle speed remains stable and at the RPM specified by the manufacturer.
Note that the idle air control valve is closed by the PCM when the throttle valve is opened. This is done in order to prevent excess air from entering the engine.
Decoding errors
Each code consists of five characters: P 1 4. Let's say right away about the fourth and fifth characters - they indicate the serial number of the error. Now it’s worth taking a closer look at what the codes consist of
The first character may vary depending on the vehicle system:
- P – malfunctions in the operation of the power plant; the symbol also indicates defects in the automatic transmission.
- U – you need to look for a fault in the interaction node between the system units.
- B – defects in the operation of body systems, which include electric lifts, airbags, etc.
- C – chassis sensors have detected a malfunction in the chassis system.
Let's move on to the second character:
- 3 – reserve.
- 2 and 1 – codes set by the manufacturer.
- – common code for on-board diagnostics (OBD-II).
The third symbol indicates to the motorist the type of breakdown:
- 1 and 2 - indicate defects in the operation of the fuel unit or the appearance of malfunctions during the air supply.
- 3 – breakdowns in the ignition unit.
- 4 – indicates auxiliary control.
- 5 – in idle mode, some components do not work correctly.
- 6 – electronic unit or its circuits.
- 7 and 8 – defects in the operation of the gearbox.
Symptoms of malfunction
The main driver symptom of P0507 is the MIL (Malfunction Indicator Light). It is also called Check engine or simply “check light”.
They can also appear as:
- The “Check engine” warning light on the control panel will light up (the code will be stored in memory as a malfunction).
- Floating speed, as well as attempts to stall at idle.
- Idle speed is higher or lower than normal.
- The engine may stall if the idle speed is not maintained by pressing the accelerator pedal.
Depending on the symptoms, the severity of a P0507 code can range from moderate to severe. Therefore, it is recommended to resolve this issue as soon as possible.
Symptoms of P0507
The most common symptom of a P0507 code is that you will notice that the idle speed is higher than normal. You will also likely see a check engine light.
There may be other symptoms such as misfire, rough idling and acceleration if the cause of P0507 is a lean/rich mixture.
- High idle speed.
- Rough idle.
- RPM jumps XX.
- Check Engine.
- Uneven acceleration.
How to Troubleshoot or Reset Trouble Code P0507
Some suggested steps to troubleshoot and fix error code P0507:
- Read all data and stored error codes using an OBD-II scanner.
- Clear the codes and check if the P0507 code appears again.
- Observe the engine's operation at idle speed, with the gear engaged and disengaged. To check whether the engine idle speed corresponds to the values specified in the manufacturer's technical documentation.
- Check the engine for vacuum leaks.
- Inspect the throttle body for carbon buildup. And also on the body and inlet of the idle air bypass control valve.
- Disconnect and check the idle air control valve.
- Check if the idle air control valve passages are clogged.
How to Diagnose Code P0507
This diagnostic method is used by the most professional auto mechanics. Some tools may be required to complete these tasks.
Always connect the car charger before using the OBD2 scanner and other diagnostic tools. Low voltage can damage control units and lead to errors.
- Connect the OBD2 scanner, read the P0507 code and check for other trouble codes.
- Check the current idle air control/throttle valve data to ensure it is correct. Check the accelerator pedal position sensor to ensure it is working properly.
- If there are no other stored trouble codes, check and listen for any air leaks around the intake system. If vacuum leaks are not visible or heard, you can use Quick Start aerosol or any other flammable aerosol. Gently spray it around the intake manifold while the car is idling. If the engine speed increases while spraying, you have a leak somewhere in that area. Remember to exercise caution and always have a fire extinguisher nearby. Professional mechanics use smoke generators to quickly and easily find such problems without the risk of fire.
- If no leaks are found, check to see if the throttle body is dirty. If you find it dirty, remove it if possible and clean it with brake cleaner or any other strong product. Make sure the throttle body is 100% clean.
- After cleaning the throttle body, it is usually necessary to perform a basic tuning and throttle adaptation reset to learn the new values for the clean throttle body. You can do this using an OBD2 scanner. The cheapest scanners will not be able to do this, it may require a dealer OBD2 scanner that fits your car model. Always check if the OBD2 scanner is compatible with your car before you buy anything.
- Clear the P0507 code and take a test drive to make sure the P0507 code goes away.
- If P0507 still returns, check the EVAP, IAC, EGR, PCV valves, etc. These are more advanced work.
Diagnosis and problem solving
Connect the scanner, read and write down all available codes. This information may be useful if an intermittent fault is later diagnosed.
If other codes are present along with P0507, diagnose and resolve them in the order in which they were stored. The most likely additional codes are usually related to the vacuum system.
Therefore, check the vacuum system for leaks caused by damaged vacuum lines. If necessary, repair and clear all codes before operating the vehicle. Then, retest the system to see if any codes are returned.
Throttle valve
If the code persists, remove the throttle body from the intake tract and inspect it for excessive carbon deposit buildup. In some cases, it may be possible to remove light carbon deposits from the throttle body and auxiliary air passages using approved cleaners.
However, heavy deposits usually cannot be removed without damaging the throttle body or idle air control valve. In these cases, the best option is to replace the throttle body or idle air control valve with original parts.
When installing cleaned or replaced parts, ensure that all seals and gaskets are also replaced to prevent vacuum leaks. Double check all vacuum line connections before starting the engine or operating the vehicle.
Checking wires and connections
If the P0507 code persists, perform a thorough visual inspection of all associated wiring. Look for damaged, burnt, shorted or corroded wires and connectors.
Once no visible damage is found, check resistance, ground, and reference voltage. Compare all readings obtained with the data specified in the manual. Replace wiring as necessary to ensure all readings are within manufacturer specifications.
Stepper motor and idle control valve
Check the actual signal voltage that reaches the stepper motor at the connector. Using a scanner, command the idle air control valve to open. Compare the obtained value with the values specified in the manual.
Special diagnostic programs usually produce a voltage range that corresponds to the degree of opening of the idle air valve. And sometimes the degrees of rotation of the stepper motor.
These readings must correspond exactly to the stated values, otherwise the harness must be replaced. If all readings obtained are consistent with the stated values, the stepper motor is faulty and must be replaced.
These steps should solve the problem with error P0507. But if it still appears again, then perhaps the problem is periodic. In such a case, diagnosis can be challenging. And sometimes it is necessary to give the malfunction a chance to worsen in order to understand exactly where the problem is.