How to check car suspension springs
The question of how to check a spring is often of interest to car owners only when the car “sags” even with a small load, or even without it. However, such a check of the suspension springs should have been done only when the first symptoms of their wear appeared. It is best to do diagnostics in a car service center on a special stand, but the simplest check of the condition of the springs can be done in a garage with your own hands. This does not require a special tool, and the procedure is accessible to almost everyone.
Where to buy Patron suspension springs?
Today, the market offers a wide range of auto parts from various manufacturers, which makes it difficult for consumers to decide on a brand and choose a truly high-quality product. The prices for original spare parts are quite high, and not every driver can afford to purchase them. Among the available alternatives, which are not inferior in quality to the original ones, PATRON spare parts, our own brand, stand out. You can purchase Patron suspension springs, as well as other automotive components, in the company’s stores, as well as at points of sale from official dealers of the brand.
Patron auto parts undergo strict quality control during the production process, which is confirmed by numerous certificates. Suspension springs of this brand are made exclusively from high-quality raw materials in compliance with all requirements for production technology. Car owners who purchase PATRON parts note their reliability and wear resistance.
From the outside, checking a car's suspension seems like a complex process that requires global technical knowledge and equipment proficiency. In fact, it is possible to check the suspension yourself - this does not require equipment or complex instruments. We will tell you in this article how to properly check the suspension yourself, and what conclusions you can draw after checking.
Signs of faulty suspension springs
For the need to check the fatigue of car suspension springs, one or more signs may appear. Among them:
- It is visible to the naked eye that one of the sides of the car “sank” more than the other in an unloaded state (without cargo and passengers). You need to look at one axis, that is, for example, compare the front left and front right springs. In such cases, most likely the spring has sagged or broken completely (on the sagging side). However, there is a nuance here, which consists in the fact that the subsidence of one or the other side can be influenced by the so-called glass, that is, the place where the spring rests. Often on old cars (most often VAZ “classics”) the glass falls through. When diagnosing, you will need to check both the fatigue of the spring and the cup.
- A metallic clanging sound while driving on rough roads is a clear sign of a broken suspension spring. Moreover, this clanging sound can be produced even when driving over small bumps or potholes. However, in this case it makes sense to also check the steering rack and ball. A metallic clanging sound usually indicates that one of the spring coils has partially or completely snapped.
- Low landing of the machine when loading, even lightly. Especially if everything was fine before and such a phenomenon was not observed. Typically, this problem is more common on the rear springs, and at the same time the wheels begin to scrape against the wheel arch liners, and the mud flaps begin to touch the road surface. This is a very dangerous situation, because in this way, in emergency mode, the tires wear out, and at one “wonderful” moment they can simply burst.
- Strong vibration and shaking while the car is moving, even on a flat road. In this case, the shaking increases as the speed of the machine increases. As a rule, this is a sign that the spring has burst completely.
- Reduced ride quality . This can be seen by comparing the operation of the machine before and after the problem occurred. Usually the spring stops working normally and when driving over bumps the car jumps or dives into a hole.
- Significant car roll even with gentle braking.
If at least one of the above symptoms appears, it makes sense to perform a comprehensive diagnosis of the suspension, including checking the shock absorber springs. Moreover, it is advisable to perform the check not only on the side where the car sank, but on all the others too.
Why a spring on a car burst: causes, signs and consequences
How old springs can quickly “kill” shock absorbers and suspension: review and solution to the problem
Did you know that motorists are increasingly faced with one extremely interesting problem, which is not only difficult to identify during a technical inspection, but is not always possible to feel after an immediate breakdown? What kind of problem is this peculiar? It probably occurs in a very small and unimportant system of the car. Well, if you only consider that a car is an insignificant and unimportant detail...
Yes, as it turns out, more and more often owners of old cars are faced with breakdowns of the suspension springs of their cars. But this is only one side of the problem. According to the second, there are already frequent cases of springs breaking on relatively new cars, literally a few years after the car leaves the factory gates. Moreover, the first signs of the beginning epidemic of breakdowns were found in Europe, which is relatively good in terms of road quality. In particular, the problem is observed in Poland.
So what happens to one of the main suspension elements? But before answering this question, let’s first quickly remember what a car spring is and why it is needed.
Springs play a very important role in the suspension, because we are talking about suppressing shocks and overloads caused by the movement of unsprung masses (wheels, suspension elements), that is, ensuring comfort while driving, safety and maintaining a given ground clearance under the bottom of the vehicle.
Springs also reduce. Without springs, the car would be completely impossible to drive. For example, without shock absorbers, at the very least you can drive slowly, but without springs this is almost impossible! So why is such an important element talked about so little in reviews? Why don't they pay him enough attention?
Everything is quite prosaic. First, since coiled elements do not require maintenance, they wear out very slowly, and until mechanical and very significant damage occurs, it will be difficult for the driver to feel the difference when driving between a new spring and one that has traveled a hundred or two thousand kilometers.
Yes, the car will slowly lose ground clearance all this time, but that seems to be the whole difference. You are unlikely to feel any mechanical deterioration in handling.
The tag will tell you that these springs were on the car from the very beginning.
But what’s more interesting is that even cracking of the spring coils cannot cause major complications in the car’s handling, since damage usually occurs at the very end of the winding, at the place where the spring is fastened to the body or suspension, the so-called spring socket.
In addition, the length of the spring itself does not change significantly even after breaking, until both parts of the spring move relative to each other. Only after this the height of one of the wheels drops slightly, which, however, may also go unnoticed by the motorist.
Why do springs break, symptoms of failure?
The spring looked almost new
The working environment of the suspension spring can be called complex, so during operation it is easy to damage the protective coating of the coiled body of the element and expose the steel, which can very quickly begin to corrode under the influence of salts. But most of all, the spring element suffers in winter, when water, salt and sand get between the coils, which leads to its damage.
Typical symptoms of a broken suspension spring:
Irregular knocking and vibration on uneven surfaces; Characteristic dull knocks when the wheels are turned strongly or when braking heavily; There is a difference in the height of the machine along the longitudinal axis (the left side is higher than the right, and vice versa) or between the front and rear parts; Strong rolls when driving and braking
Why might springs need replacement?
If you bought a car that has springs other than black, then you will probably have to say goodbye to this tuning. Most likely, after replacing them with standard elements, the car will become more comfortable and will last longer.
Evgeniy Lomarev, an employee of the AI-Engineering Auto service center, gives the following useful tips:
“If your car is 10 years old or more, it is advisable to install new springs all around. I advise many auto mechanics to do this, and I am no exception. The fact is that over time, deformation of the spirals occurs, fatigue accumulates in the metal, sagging of the springs or other irreversible degradation occurs. Over time, not only comfort, but also travel safety will deteriorate; the wheel no longer quickly returns to the supporting surface (road surface).”
The specialist also assures that it is important to remember about the problems associated with exceeding the maximum load on cars and their operating environment. Although chronic overload can quickly destroy the springs, driving on bad and broken roads will also most likely require you to write off the springs much earlier than planned. In the worst cases, the springs will expire in 3-5 years with low mileage.
“It is recommended to replace springs every second shock absorber replacement, 80-100 thousand km. In other words, on a 4-5 year old car with an average mileage of 20 thousand km per year, the springs should ideally be replaced (once), as well as the shock absorbers (twice).
However, there are always exceptions to the rules, and for careful drivers who do not operate the car in winter or snowy weather (for example, in the south of the country), and also drive on unbroken asphalt, these suspension elements can go much longer without breakdowns.
But don’t forget, every 15-20 thousand. kilometers, pay attention to the car’s suspension, checking its condition.”
Evgeniy also shared another interesting observation. As it turned out, spare parts installed on a new car on the assembly line during normal operation without accidents generally last much longer than even the expensive analogues installed by motorists on their cars when replacing them. Perhaps there is an explanation for this: do they use higher quality parts in production?
In practice, cars drive on dead springs for 200-250 thousand km. At the same time, motorists don’t even suspect that sagging springs simply destroy delicate shock absorbers, causing them to fail 2-3 times faster!
Springs should also be replaced with new ones, even in cases where severe corrosion is visible to the naked eye. In general, this is a common occurrence and one of the most popular causes of cracks. More often, springs break only due to poor quality products or when purchasing counterfeits. Therefore, it is better to buy them from well-known companies.
Do I need to change springs as a set for all wheels?
Wheel torn by a piece of spring
see also
This question cannot be answered unambiguously. On the one hand, many experts recommend replacing the entire set of springs in a circle. On the other hand, if you are the owner of a front-wheel drive car, then most likely the rear springs and shock absorbers of your car will last 1.5-2 times longer than the front elements. There will simply be less load. This means that if the springs are not rusty, why replace them with new ones? All you have to do is change the front ones and move on!
However, to determine this, you need to go to a service station and study the suspension in detail. Maybe the seemingly prosperous spring has already burst and this is really an epidemic...?
Information publication: Traffic police news, accidents, traffic fines, traffic police, Online traffic rules exam. Technical inspection
Causes of spring failure
There are five main reasons why rear and/or front springs fail completely or partially.
- Metal fatigue and spring wear . This happens for natural reasons over time. During operation, the metal becomes softer and more pliable, and accordingly, the spring becomes softer. And also when the coils of the spring collide, the springs rust and microcracks appear. Particularly harmful to the rods are the strong impacts that occur when a car hits a pothole or bump at high speed.
- Constant friction of the coils of a weakened or heavily loaded spring among themselves. For this reason, the spring stiffness decreases, and the surface of the coils themselves becomes not round, as it was initially, but has a worn-out plane. Accordingly, for this reason the rod becomes thinner, and therefore the spring becomes weaker.
- Overloading a car and driving it in this condition at high speed over uneven surfaces or distances. In such conditions, all suspension elements suffer, including springs.
- Corrosion of metal springs . This is a very common reason why springs fail. Over time, the paint on their surface peels off, and water and road reagents do their job. Interestingly, if corrosion “ate” only a 0.15 mm layer on a 10 mm spring wire, then the cross-section of the said wire is reduced by as much as 6%!
- Installing the wrong spring . In particular, this can happen due to incorrect selection of parts. Another option is a factory defect. It often happens that springs with different stiffnesses are placed in one package.
Stretched spring - reasons
If the spring is faulty, this does not mean that it is of poor quality or that you have been deceived. There are a number of factors that are involved in premature spring failure, including:
- Natural wear and tear. Too frequent use in difficult conditions or simply high mileage. Nothing lasts forever, perhaps the spring has simply exhausted its resource. Each spring has its own resource, approximately 50-80 thousand km. mileage
- Incorrect operation. If you constantly load your car or carry more weight than expected, the springs will last much less than if you were driving alone or with minimal additional weight.
- Corrosion and reagents. These factors need no introduction or explanation. Once the rust penetrates under the paint of the spring, it does its dirty work, day after day, eating away at the surface of the spring, weakening it. The same is with reagents; they aggressively affect the metal, destroying its surface and worsening its properties.
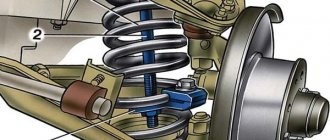
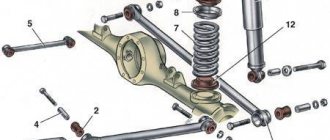
How to check a suspension spring
To check the condition of the car suspension spring, it must first be removed from its seat and cleaned of dirt and rust. This will allow you to visually assess its condition, check for cracks, chips and other defects.
First of all, you need to check the spring for stiffness. However, before that you need to find out what class it belongs to, as well as which springs the car manufacturer recommends installing on the part of the suspension from which it was removed.
All springs are divided into two main classes - A and B. Their differences are in stiffness and length. The length of A-springs is up to 27.8 cm, and the length of B-springs is over 27.8 cm. As for color coding, this depends on the specific car brand and spring manufacturer.
Press check
To determine the fatigue of springs using the compression method, you need to know what stiffness it should be installed in a specified location in order to know with what to compare the result obtained in the future. So, in garage conditions, spring stiffness can be checked using the following tools:
- two square bars with a thickness of at least 1.2 cm and an area slightly larger than the area of the end of the spring being measured;
- scales;
- manual press (controlled by a thread drive).
The verification algorithm in this case will be as follows:
- Using a floor scale, find out the total mass of both bars and the spring being measured.
- Place the floor scales on the lower platform of the press, place one of the pre-prepared bars on them.
- Place a spring on the block, and place a second block on top of it.
- When activating the press, it is necessary to compress the spring.
- The compression value (distance) and pressure must be pre-selected in accordance with the documentation. Accordingly, there can be no specific recommendations here.
- From the obtained force value (in kilograms of force), it is necessary to subtract the previously measured total mass of the bars and spring.
If the spring has compressed a certain distance with insufficient force, this indicates that it has weakened significantly and it is advisable to replace it. However, the decision to replace must also be made on the basis of a visual inspection, as well as information about how many kilometers the car has traveled with a given spring.
However, in practice, this method is quite problematic to implement, since the test requires considerable effort. For example, when testing the springs of a VAZ-2110 car, you need to develop forces equal to 325 kilograms of force. With this value, standard front suspension springs must have a length of at least 201 mm (for the so-called “European” spring, the same value will be 182 mm). For a rear standard spring with the same force, its length will be at least 233 mm (for a “European” spring - at least 223 mm).
Theoretical calculations
The permissible geometric change of the spring, as well as its stiffness, can also be calculated using the appropriate formulas. Thus, the geometric change is calculated as follows: X = F × L / C. Here X is the change in spring size, F is the applied force, L is the initial length of the spring, C is the proportionality coefficient, table value (depends on the radius of the coil part of the spring, material its manufacture, rod diameter).
Similarly, the stiffness of the spring is calculated using another formula - k = F / X. Here, too, F is the force, and X is the size of the compressed spring measured as a result of experiment. The complexity of such calculations is due to the fact that you need to know the proportionality coefficient, and this information can only be found in technical documentation.
Checking the manual
The technical documentation (manual) for any car contains a detailed description of the procedure for checking ground clearance, and, in particular, springs. Let's consider a similar diagnosis using the example of the popular Toyota Camry. So, for this you first need to measure four parameters:
- A is the distance (clearance) from the center of the measured front wheel to the surface on which the machine is installed;
- B - distance from the center of the bolt of the lower suspension arm No. 2 of the measured front wheel;
- D — distance from the center of the measured rear wheel to the ground (clearance);
- C is the distance from the center of the trailing arm bolt of the corresponding rear wheel being measured to the ground.
Next, you need to find the difference between the values of A and B, as well as C and D. After this, compare the minimum acceptable values with the data given in the table. If the values obtained as a result of measurement are lower than those given in it, then it is necessary to carry out additional diagnostics. You may have to use additional spacers or replace the spring with a new one. If the obtained values are greater than the minimum acceptable values, it means that everything is in order with the spring (if there are no additional symptoms of a malfunction).
Do I need to change springs as a set for all wheels?
A wheel torn by a piece of a spring.
See also : What is the radius of the running shoulder, and why is it important?
This question cannot be answered unambiguously. On the one hand, many experts recommend replacing the entire set of springs in a circle. On the other hand, if you are the owner of a front-wheel drive car, then most likely the rear springs and shock absorbers of your car will last 1.5-2 times longer than the front elements. There will simply be less load on them. This means that if the springs are not rusty, why replace them with new ones? All you have to do is change the front ones and move on!
However, to determine this, you need to go to a service station and study the suspension in detail. Maybe the seemingly prosperous spring has already burst and this is really an epidemic..?
Shock absorber malfunction: symptoms and what affects
Shock absorber malfunctions greatly affect the car's behavior on the road. In particular, the car body “dives” during acceleration and braking, the braking distance increases, rolls heavily during maneuvering and sways when driving over uneven surfaces.
There are obvious and hidden signs of faulty shock absorbers. Obvious ones include the appearance of oil leaks (wear of the oil seal and/or rod), but there are more hidden ones, for example, aging of the oil, deformation of the valve mechanism plates, wear of the piston seal and the inner walls of the working cylinder. To avoid unpleasant consequences, you need to identify the faulty shock absorbers in time.
Signs of faulty shock absorbers
There are two types of signs that a shock absorber has completely or partially failed. The first type is visual. In particular, they can be identified by visual inspection of the shock absorber. The second type of signs includes changes in the behavior of the car in motion. Let us first list the signs related to the second type, since first of all it is necessary to pay attention to how the behavior of the machine has changed, in particular:
- Rocking when braking and accelerating . If the shock absorbers are working properly, then even with sharp braking the car should swing back no more than once, after which the shock absorber should dampen the oscillatory movements. If there are two or more swings, this is a symptom of partial or complete failure.
- Roll when maneuvering . Here the situation is similar; after exiting a sharp roll when entering a turn, the body should not sway in the transverse plane. If so, the shock absorber has similarly failed.
- Increased braking distance . This factor is due to the same swing during braking. That is, during prolonged braking, the shock absorber does not dampen vibration, and the car periodically lowers and raises the front part of the body. Because of this, the load on the front wheels is reduced, which reduces braking efficiency. The braking distance is especially longer for vehicles equipped with an anti-lock brake system. This is because the rear end rises and the ABS reduces the brake line pressure. Also, the braking distance increases when braking on uneven roads.
- The car does not “hold” the road . In particular, when the steering wheel is installed in a straight position, the car constantly pulls to the side. Accordingly, the driver must constantly steer in order to align the trajectory of movement.
- Discomfort when driving . It can manifest itself in different ways. In particular, some drivers and/or passengers feel discomfort from the rocking of the car when driving long distances; people suffering from “sea sickness” (the official name is kinetosis or motion sickness) can feel motion sick. This effect is a typical symptom of faulty rear shock absorbers.
Please note that signs such as long braking distances, uneven tire wear and constant need to steer may indicate other problems in the vehicle, such as worn brake pads, low brake fluid levels, uneven tire pressures, problems with the ball joint or other components. pendants. Therefore, it is advisable to perform a comprehensive diagnosis. Visual symptoms of shock absorber wear include:
- The appearance of drips along the body and stem. In particular, this occurs due to wear of the oil seal (seal) and/or shock absorber rod. A decrease in oil level leads to a decrease in the operating amplitude of the device, as well as to an increase in wear of the parts included in its design.
- Wear of silent blocks. As is known, in this rubber-metal hinge, mobility is ensured due to the elasticity of rubber (or polyurethane, depending on the design). Naturally, if the shock absorber works hard, then increased forces will be transferred to the silent block, which will lead to its significant wear and failure. Therefore, when diagnosing shock absorbers, it always makes sense to check the condition of the silent blocks.
- Damage to the shock absorber housing and/or its fasteners. This can be expressed in different ways. For example, the appearance of rust on the rod (stand, support), curvature of the body, damage to the mounting bolts, and so on. In any case, the shock absorber must be carefully inspected.
- Uneven tire wear. They usually wear more on the inside and less on the outside.
That is, if there is a malfunction of the shock absorbers, then expect failure of other suspension elements, because they are all interconnected and can be influenced by each other.
avtoexperts.ru
It's no secret that the suspension experiences serious shocks due to the quality of the roads. And in order to somehow minimize the impact, springs are installed. They affect not only the main parameter, such as the height of the body above the ground, but also allow you to keep the car at a practically specified height, even taking into account the cargo taken on board. In addition, there is an opinion that the effect of springs on the suspension as a whole is favorable, and the handling of the car improves.
Remember that the design of all springs is generally identical, the only differences that may be are the stiffness indicator and the type of shape of the products themselves.
Keep in mind that depending on the type of part, roll in turns may exceed the permissible 3-4 degrees. With properly selected springs, this indicator remains at a level of no more than two degrees. Therefore, it is very important to choose the right element that will correspond not only to the nature of your driving, but also to the basic requirements of the manufacturer for a particular model.
Also, don't forget that part of choosing the right spring depends on where exactly it is being installed. After all, there are two placement options - on a stand and separately.
Spring in shock absorber strut
For example, often, when the shock absorber and spring are located separately, barrel-shaped and conical shapes are chosen.
shock absorber separate from the spring Hyundai Getz
But for installation on racks, preference is given to coil springs. The true reason for this “policy” of manufacturers is not known, but there is an opinion that this format is due to the fact that the racks are usually installed at right angles. And when the arrangement is separate, a small angle is provided, and in this case, the cone and “barrel” make it possible to “eliminate” the tension when the spring “plays” on bumps and when sagging due to overload.
In general, you can notice this pattern: when a joint pair of struts and springs is installed, the main emphasis is on rigidity and ground clearance. But, you must also take into account that stiffer springs can be used. Regarding the separate location, shock absorption occurs along several trajectories, depending on the modification. Which is why many claim that the split type is more suitable for driving on bumpy roads and in the city; the cabin is comfortable, because in this case, the suspension handles multidirectional impacts better.
Hardness, how to determine?
First, let's establish what a spring is? This is a mandatory component of the suspension, which is presented as a certain elastic element. It provides mitigation of impacts and jolts, including during sudden braking and starting. The purpose of the spring is to return the wheel to its original “position” as quickly as possible after hitting an obstacle.
A part that is too rigid significantly impairs the car's handling, especially on rough roads. However, the advantageous side of increased rigidity is greater safety when driving at high speeds. That is, it does not allow the body to sway as much as if it were too soft. The latter cope with almost all potholes without discomfort for the driver, but with such springs it is difficult to take turns.
Remember, there are several main factors that affect stiffness. Knowing them, you can independently determine the type of your own element installed on the suspension. So:
1. The diameter of the rod itself. Remember an important rule: the thicker the rod, the stiffer the part.
2. Spring diameter on the outside. The larger the diameter, the lower the actual stiffness.
Lowering springs for BMW E63
3. Form. There are several main types: conical, cylindrical, barrel-shaped. Each variety has its own characteristics and characteristics. There are also combined ones.
Spring forms
4. Number of turns. The rule is this: the more turns, the less rigidity there will be.
Hardness is determined quite simply. In most cases, the manufacturer independently applies markings that make it clear which class the product belongs to.
Example of hardness marking by color
Remember that the yellow marking indicates a length of up to 240 mm. But, basically, all the indicators that are required to calculate stiffness are on the product.
Example of color coding
If no markings are found, the indicator can be calculated as follows. So, prepare scales (regular floor scales), a wooden block, a ruler, and the product itself. You need to place the block on the scale, but remember that the width of the board must be greater than the diameter of the spring. Next, we take the second board and press it on top and measure the length of the product, naturally, without taking into account the boards. Either independently or using a special press, the spring must be compressed to a certain level. As a rule, this is 40 mm. Record information from the scales. Next, having the initial length in the expanded and compressed positions, we calculate the difference. Next, you need to divide the resulting weight after compression by the difference, thereby obtaining a stiffness indicator.
There are more complex methods of calculation, but it’s not worth talking about them, because at least two more values are required, which can be derived if you know Hooke’s formulas and laws, as well as the theory of proportionality. For an ordinary driver, this method of calculation is superfluous; it can be found out much easier.
Resource, and which ones are better to choose?
As a rule, among the most popular queries in search engines is what is the mileage of springs, and which ones are better to choose? It is difficult to judge which ones are better, because each motorist has his own preferences in this regard. Some people like to drive fast and have strict safety requirements, while others prefer comfort. Everything is individual, moreover, today there are a huge number of manufacturers who can offer universal springs, including so-called adjustable ones.
Adjustable spring kit
What, in principle, should be understood by the word regulated? It just seems to you that everything is simple, but they can still differ from each other. There are two types:
• With an adjustable “nut”, which is screwed onto the cylinder and allows you to either increase or decrease the rigidity depending on the “twisting”.
• With an adjustable spacer, in principle, many of these two points are not even separated
What resource? It is difficult to answer in the affirmative about the service life, because everything directly depends on the quality of the roads. In some places the springs last 100,000 km, but in others they don’t last even 10,000 km. In general, it can be noted that the greater the rigidity, the more durable it is, and vice versa. The average “mileage” rarely exceeds 50,000 km.
Malfunctions and their symptoms
There are not many faults as such; in fact, the design part of this element is not complicated. The following types of problems are divided:
• Bar breakage at the edges.
• Trivially “tired” metal.
• Broken coil.
Spring breakage
In general, that’s all, there’s nothing more to add. Either the spring sagged due to frequent overloads, or the coil burst, that’s all.
What are the signs of trouble? A wide range of features can be noted here:
1. Reduced lumen (clearance).
2. The appearance of vibration or knocking.
3. Car rolliness. That is, a situation when, when braking and starting, the car “bites”.
4. “Breakthroughs” of the suspension. When, when hitting bumps, holes, “humps,” metal elements touch each other, for example, coils. In working products, this should not happen.
5. Large rolls in corners.
6. Discrepancy in the height of the front and stern.
The reasons for all this are varied.:
• Wear and tear due to old age.
• Incorrect operation (transportation of large loads).
• Reagents and chemistry in general.
What is the effect of a faulty shock absorber?
The use of worn shock absorbers can not only cause discomfort while driving, but also cause a real danger when driving the car. So, possible problems associated with a faulty shock absorber:
- Reduced wheel grip. In particular, when the car rocks, the clutch will have a variable value.
- Increased braking distance, especially on vehicles with an anti-lock braking system (ABS).
- Some electronic systems of the car, such as ABS, ESP (exchange stability system) and others, may not operate correctly.
- Deterioration in vehicle handling, especially when driving at high speed.
- The appearance of “hydroplaning” when driving on a wet road at low speeds.
- When driving at night, constant rocking of the front of the car can cause the headlights to blind oncoming drivers.
- Discomfort when driving. This is especially true when driving long distances. For the driver, this threatens increased fatigue, and for people prone to seasickness, this is dangerous due to motion sickness.
- Increased wear of tires, rubber bushings, silent blocks, bump stops and springs. and other elements of the car suspension.
What are shock absorbers and springs
The shock absorber and spring are an inseparable duet. Their main task is to make the car run as smoothly and under steering control as possible. The spring, due to its elasticity, smoothes out the shaking and shocks that are inevitable when the car moves over uneven roads. When a car hits a pothole at any speed, the wheel jumps up.
For a moment there is a loss of adhesion between the rubber and the road surface. The spring's job is to push the wheel down to the road as quickly as possible, because the "bounce" locks the steering. But the spring doesn't just push down. It makes oscillatory movements, extinguishing the impact energy. The number of vibrations depends on the elasticity of the spring. The softer the steel from which the iron spiral was made, the stronger the compression and damping of impact energy.
Causes of shock absorber malfunction
The causes of failure are usually natural factors, including:
- Aging of shock-absorbing fluid (oil). Like other technological fluids in a car, the oil in the shock absorber gradually gains moisture and loses its performance properties. Naturally, this leads to the fact that the shock absorber begins to work harder than it worked before. However, it must be understood that fluid aging does not happen overnight, with the exception of a rupture of the seal on the shock absorber body.
- Torn seal. In particular, the sealing of the piston and the inner walls of the working cylinder. The oil seal can rupture due to external factors or simply due to the aging process. It, like any rubber seal, becomes tanned over time and begins to leak liquid. Because of this, oil leaks from the shock absorber, as well as moisture from the outside entering the oil, which leads to a deterioration in its performance.
- Deformation of the valve mechanism plates. This process is also natural and occurs on an ongoing basis, albeit at different speeds. Thus, the rate of deformation depends on two main factors - the quality of the shock absorber (the quality of the metal of the plates) and the operating conditions of the machine (naturally, a significant impact load leads to premature deformation).
- Gas leak. This is true for gas-filled shock absorbers. The idea here is the same as for oil-filled devices. Gas here performs a damping function, and if it is not there, then the shock absorber will not work.
- Failure of silent blocks. They wear out due to natural reasons, losing their elasticity and performance. These components are practically not subject to repair, so if they fail, they simply need to be replaced (if possible, or the shock absorbers must be completely changed).
When is the right time to change suspension springs?
- If they break (usually the break occurs in the lower or upper turns);
- Pronounced corrosion and serious cracks ;
- The height of the body has decreased significantly, the wheels “rub” against the arches .
You can fully evaluate the elasticity and possible defects of the springs when disassembling the rack. To do this, experienced craftsmen can use conventional tools (spanners and socket wrenches, hammer, screwdriver), but professionals also use a clamp - a vice to compress the coils and remove the cup. If you decide to disassemble the shock absorber strut, it will be easy to use a simple ruler to measure the degree of shrinkage of each spring compared to the factory values.
If your suspension has begun to handle bumps poorly, but you don’t yet think it’s time to change the springs, you can strengthen them with MRoad brand buffers . Buffers are interturn cushions made of polyurethane that increase the elasticity of the suspension, improve driving characteristics and prevent the body from sagging. They are inserted into the middle turns and prevent them from contracting completely, while taking part of the blow upon themselves. Motorists using MRoad buffers note improved handling, an increase in ground clearance by up to 2 cm , a smoother ride on bumps, and most importantly, the absence of breakdowns.
How to determine if shock absorbers are faulty
Car owners are not without reason concerned about the question of how to check an oil or gas-oil shock absorber. This is due to the fact that modern shock-absorbing devices often have a more complex design than older models, which makes diagnostic measures more complicated. Therefore, ideally, they should be checked in a car service center on a special stand. However, there are a number of “garage” verification methods.
Body rocking
The simplest, “old-fashioned” method is to rock the car body. In particular, they rock its front or rear part, or the shock absorbers separately. You need to swing it strongly, but do not bend the body elements (in practice, such cases occur!). In theory, you need to achieve the maximum possible swing amplitude, then release the body and look at its further vibrations.
If the shock absorber is working properly, the body will make one swing (or one and a half), after which it will calm down and remain in its original position. If the shock absorber has a malfunction, the body will make two or more oscillations. In this case, it must be replaced.
It is worth noting, however, that the rocking method is suitable for cars with a simple suspension system, for example, the VAZ “classic” (models from VAZ-2101 to VAZ-2107). Modern cars often use complex (often multi-link) suspension, so it will dampen the resulting vibrations even with faulty shock absorbers. Therefore, with the help of body rocking, by and large, it is possible to determine two borderline states - the damper is completely out of order, or it jams during operation. It is not easy to identify the “average” states of the shock absorber using swinging.
Visual inspection
When diagnosing a problem shock absorber, be sure to perform a visual inspection. To do this, you need to drive the car into a viewing hole or lift it on a lift. You can, of course, dismantle the shock absorber, but this can take a lot of time and effort. During the inspection, be sure to check for oil smudges on the shock absorber body. You can wipe off traces of oil with a rag and leave it like that for several days. After this period, the test should be repeated.
If the car is raised on a lift, it is advisable to check the condition of the shock absorber rods. They should not show any signs of rust or damage. If they are present, then the device is at least partially faulty and additional diagnostics need to be performed.
When inspecting, be sure to pay attention to the wear pattern of the tires. Often, when shock absorbers are broken, they wear unevenly; as a rule, the main wear occurs on the inside of the tire. There may also be isolated bald spots of wear on the rubber. However, tread wear may also indicate other failures in the suspension elements, so additional diagnostics are also needed here.
If faults in the front shock absorber (strut) are checked, a mandatory inspection of the springs and upper supports must be performed. Shock-absorbing springs must be intact and free of cracks and mechanical damage.
Machine control check
If the shock absorber/shock absorbers are faulty, then while driving the driver will feel that the car is “scouring” along the road, that is, it will be necessary to constantly steer in order to keep it in the rut. When accelerating and braking, the car will sway. The situation is similar with lateral body tilts. In this case, it is not necessary to accelerate to a significant speed; the city speed limit is quite suitable for testing. In particular, at a speed of 50...60 km/h you can do sharp acceleration, braking, and snake.
How old springs can quickly “kill” shock absorbers and suspension: review and solution to the problem
Did you know that motorists are increasingly faced with one extremely interesting problem, which is not only difficult to identify during a technical inspection, but is not always possible to feel after an immediate breakdown?
What kind of problem is this peculiar? It probably occurs in a very small and unimportant system of the car. Well, if you only consider that the springs of a car are an insignificant and unimportant detail... Yes, as it turns out, more and more often, owners of old cars are faced with breakdowns of the suspension springs of their cars. But this is only one side of the problem. According to the second, there are already frequent cases of springs breaking on relatively new cars, literally a few years after the car leaves the factory gates. Moreover, the first signs of the beginning epidemic of breakdowns were found in Europe, which is relatively good in terms of road quality. In particular, the problem is observed in Poland.
So what happens to one of the main suspension elements? But before answering this question, let’s first quickly remember what a car spring is and why it is needed.
Springs play a very important role in the suspension, because we are talking about suppressing shocks and overloads caused by the movement of unsprung masses (wheels, brakes, suspension elements), that is, ensuring comfort while driving, safety and maintaining a given ground clearance under the bottom of the vehicle.
Springs also reduce the forces acting on the suspension. Without springs, the car would be completely impossible to drive. For example, without shock absorbers you can at least drive slowly, but without springs it is almost impossible to do this! Why is such an important element discussed so little in reviews? Why don't they pay him enough attention?
Everything is quite prosaic. First: since coiled elements do not require maintenance, they wear out very slowly, and until mechanical and very significant damage occurs, it will be difficult for the driver to feel the difference when driving between a new spring and one that has traveled a hundred or two thousand kilometers.
Yes, the car will slowly lose ground clearance all this time, but that seems to be the whole difference. You are unlikely to feel any mechanical deterioration in handling.
The tag will tell you that these springs were on the car from the very beginning.
But what’s more interesting is that even cracking of the spring coils cannot cause major complications in the car’s handling, since damage usually occurs at the very end of the winding, at the place where the spring is fastened to the body or suspension, the so-called spring socket.
In addition, the length of the spring itself does not change significantly even after breaking until both parts of the spring move relative to each other. Only after this the height of one of the wheels drops slightly, which, however, may also go unnoticed by the motorist.