What is a fuel pressure regulator?
The fuel pressure regulator (FPR) is a vacuum valve; it transfers excess fuel through a return hose into the fuel tank. The RTD is a housing that contains a valve, a membrane and a spring. There are also three terminals in the housing: two terminals for the passage of fuel through the regulator, the third is connected to the intake manifold. As engine speed increases, the vacuum created in the manifold (at the third terminal) overcomes the force of the spring and moves the membrane, thereby opening the valve slightly. Excess fuel gets access to the second outlet and goes back to the gas tank. An RTD is often also called a check valve.
As a rule, the check valve is located on the fuel rail; it can also be embedded in the fuel return hose of the power supply system.
Causes of fuel pressure regulator malfunctions
RDT may fail for several reasons. For example, defective parts are found on Russian-made cars. There are significantly fewer defects on foreign models, but you can purchase a defective RTD by purchasing a non-original spare part.
Mostly the check valve breaks down due to natural aging. Let's say this can happen after a hundred thousand mileage or more. It should be noted that check valve failures are not common. Most often, in an RTD, the membrane dries out over time, less often the valve jams, and even less often the spring breaks or weakens.
Sensor failure may occur due to low-quality gasoline. For example, in winter, fuel was filled with water, and water got into the regulator. If the fuel filter is not replaced on time, dirt gets into the parts of the power system, including the regulator. In this case, the RTD valve most often jams. It’s hard to imagine what could happen to the spring, but apparently, it still breaks sometimes.
Characteristic symptoms of fuel pressure regulator malfunctions
By what signs can you determine that an RDT is not working:
- the engine is very difficult to start, you need to turn the starter for a long time and at the same time keep the gas pedal pressed in order for the engine to start;
- The engine idles unsteadily or the speed is very low, the engine often stalls. At the same time, it does not gain power at all; when trying to accelerate, it results in a deep failure;
- The spam engine changes speed sharply, this is especially noticeable at idle:
- Fuel is leaking from the fuel hoses. Attempts to tighten and replace clamps and replace hoses do not help.
How to check the fuel pressure regulator for serviceability
The fuel pressure regulator is not an electrical sensor and cannot be checked using instruments. It should also be taken into account that the RDT cannot be disassembled or repaired. Someone writes that the fuel check valve can be repaired. I would like to see what it looks like and where you can buy a repair kit. Typically, RTDs are inexpensive, and even for that reason they would not be worth repairing if they were repairable.
You can verify that the regulator is working properly by checking the pressure in the fuel system. This is usually done with a mechanical pressure gauge, which is connected to the engine power system.
Measurement is carried out as follows:
- connect the pressure gauge to the fuel system;
- start the engine and look at the pressure gauge readings.
The standard system pressure for a passenger car is usually within 3 kg/cm2. When stopping the engine, the pressure should not drop immediately - the regulator closes the return flow. If the pressure gauge needle quickly goes to zero, the RTD is most likely faulty.
Another way to check: if you manage to pinch the fuel return hose while the engine is running, then if the regulator is working properly, the pressure in the fuel system should increase. The indication of the arrow of the device depends on the degree of compression. But there are foreign cars where it is impossible to clamp the return line - instead of rubber hoses there are metal tubes, or the hoses are very short.
In some cases, by squeezing the return hose, you can verify that the RTD is faulty without a pressure gauge. But this is only due to one sign - when the engine idles and does not develop speed at all. If, when the return line is compressed, all cylinders begin to work and the engine acquires the required power, then the RTD is definitely faulty and needs to be replaced.
How to check fuel pump pressure? Using an air pressure gauge
Are you a novice car enthusiast and don’t know how to check the fuel pump pressure? Then this article is for you. The pressure in the fuel system of a car is an important parameter that needs to be measured periodically. When diagnosing an engine, auto repair shops first measure the gasoline pressure, and only then carry out all other related work. This parameter determines the quality of engine operation in various modes. How to check the fuel pump pressure with your own hands? You can do it yourself in several ways. On the open market, you can find a special device that includes a pressure gauge and other components. A similar measuring device in a car dealership will cost you 1,500 rubles (+/-). By the way, when you stop at a service station, they will carry out the procedure for measuring the pressure of the fuel pump for 200-300 rubles. If you are not eager to shell out money for a measuring device or visit a service station, then there is a way to measure pressure using an air pressure gauge designed to determine the pressure in car tires.
We measure with available means: Most likely, every car owner has a pressure gauge that allows you to measure tire pressure. Therefore, this method is perfect for novice car mechanics. I would like to immediately say a small note about this method. Air pressure gauges, as a rule, are designed to measure high pressure, about 16 atmospheres. Fuel pressure gauges have limits around 6 atm. The first type of pressure gauges have small errors at the initial scale values.
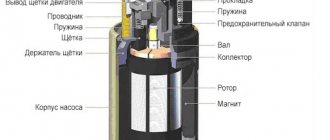
Operating principle of the fuel pressure regulator
To understand how a fuel pressure tester works, you need to know how it works. It consists of the following parts:
- Fuel pump;
- Pressure regulator;
- Electronic control unit pump;
- Fuel lines;
- Baka;
- Fuel filter;
- Injectors;
- Inertia switch.
Thanks to its design, the regulator controls and maintains the same fuel pressure relative to atmospheric pressure. Where is the fuel pressure regulator installed? Install it in the fuel tank.
Features of the device for monitoring fuel pressure in a system with fuel recirculation
The RTD is divided by a membrane into two chambers:
The valve holder itself is connected to the membrane and presses the valve to the seat. The fuel pressure, which is supplied to the chamber through special inlet passages, acts on the membrane from below. The pressure of the spring and the intake manifold acts from above. Sometimes the pressure can exceed the spring force. In this case, the valve is opened slightly, allowing gasoline to flow into the return pipeline. In this case, the pressure in the intake manifold must be taken into account.
During operation of the fuel pump, fuel leaves the tank, heading towards the filter. There it is cleaned and goes to the regulator. The regulator maintains the effective pressure in the system without stopping. The main thing is that all actions must occur correctly.
The device itself is located inside a steel case. It must also be able to withstand high pressure. The device mechanism itself consists of a diaphragm and also has a check valve. It prevents the fuel, which is under pressure, from returning to the line.
Car won't start after DIY replacement
This is a fairly common problem. It must be said that the car should not start immediately after replacing the pump. The pump first needs to create operating pressure in the system. To do this, you need to turn on the ignition for a short time (a few seconds). The key must be inserted into the lock, but not turned. The lights on the dashboard should light up. Then you can rotate the engine with the starter for five to ten seconds. If nothing works out, then you should take a break for half a minute and repeat your actions.
We recommend: Proper dilution of antifreeze concentrate
If the engine does not start even after several cranks with the starter, this indicates that shortcomings were made during assembly and connection of the fuel pump. Another reason could be a malfunction of the new pump. There is also a possibility of a planned blocking or failure of the car’s security system.
When a car owner installs and connects a new unit, various failures may occur: sticking of valves on the pump, breakage of contacts, terminals and connectors. When such problems arise, you need to try to determine their nature. Did the breakdown occur in the mechanical or electrical part of the fuel pump? The easiest way to find out is if there is a problem with the power supply. You also need to remember that the fuel filter may become clogged.
In order to accurately determine the causes of the problems, you need to make sure that the fuel rail does not contain gasoline. After this, you need to re-remove and connect the pump directly from the battery or dimensions. This method of connecting the pump is the best for quickly checking it.
A car owner must take care of every part of the car. It is best to gain knowledge about its structure and repair yourself. It is important to acquire skills in diagnosing and solving problems in the operation of individual machine systems. This also applies to the functioning of the fuel pump.
Many drivers encounter breakdowns on the road, far from cities and service points. In such a situation, you can only rely on your own experience. Knowledge about the signs and causes of malfunctions in the fuel pump will help solve problems at the initial stage of their occurrence. It will also save effort, time and a significant part of personal funds.
How does the fuel pressure regulator work? RTD operating mode
It must be remembered that the level of fuel pressure in the ramp itself depends on the vacuum in the suction manifold: the less discharge, the greater the pressure. The main mode of operation of the regulator is idle. Just at the moment of operation at this speed, the vacuum begins to reach a low point, and the pressure level in the fuel rail leads to the highest indicator. This value is applied to the regulator body in order to correctly monitor pressure during diagnostics of the supply system.
Important: if the pressure regulator cannot be repaired, it should be replaced with a new one. To avoid this, it is necessary to check it as often as possible and monitor the pressure. This will allow you to avoid breakdowns in time and save your money on purchasing another pressure regulator. There is no guarantee that the new regulator will not avoid such problems.
Important: despite the operating mode of the engine, the RTD must always respond to changes in it
Installation locations
On cars, the injection system is equipped with a separate line for draining excess gasoline, which goes from the fuel rail to the gas tank (fuel recirculation). In such injectors, the regulator is installed directly on the fuel rail (or connected to it), so the unit quickly “reacts” to changes in engine operating conditions and adjusts the pressure in the rail. In this design of the power system, a mechanical type RTD is used.
There is another version of the injector - without gasoline recirculation. In this system there is no “return” at all, and regulation is carried out at the output of their fuel pump. A feature of such a system is the location of the regulator - in the tank or near it. An RTD is already used here, the operation of which is controlled by the ECU - the control unit, through a sensor installed in the ramp, monitors the necessary parameters and corrects them by sending signals to the regulator.
Power systems with electronic regulators are used less frequently than mechanical ones due to their complex design and, accordingly, lower reliability.
Signs of a malfunctioning fuel pressure regulator
Over time, the spring in the regulator may sag without creating the necessary force. The fuel will begin to return back to the tank. This will cause a decrease in pressure in the fuel rail. Such a breakdown will lead to a lack of fuel and loss of power in the engine.
If the valve is jammed, the pressure level in the fuel frame will change differently each time. In this case, the engine will not operate regularly, and the car will twitch during acceleration.
The main symptoms of a malfunctioning fuel pressure regulator :
- Uneven engine operation;
- Stopping the engine at idle;
- A sharp increase or strong drop in the crankshaft speed at idle;
- Loss of motor power;
- Poor vehicle acceleration when shifting gears;
- Poor response to the gas pedal;
- Car choking when driving, frequent jerking;
- A sharp increase in consumption.
If you detect at least one of the above symptoms, you should immediately check the device.
Causes of malfunction of the fuel pressure regulator in a car
Cause
What is a malfunction?
The most common malfunctions include mechanical damage to the parts of this unit or clogging in its part. This leads to a malfunction of the fuel pressure check regulator. Such damage may be associated with the obsolescence of the materials from which the mechanism itself is made. In this regard, the pressure regulator returns to normal, but its operation no longer meets standard indicators. For example: vacuum disturbances occur in its closed cavity, which makes it impossible for the engine speed controller to control the engine speed. A weakened inner spring causes low fuel line pressure.
Diagnostics and malfunctions of the fuel regulator
Fuel pressure regulator
The design of the fuel pressure regulator does not allow for repairs. In some cases, it is cleaned, but this procedure does not briefly extend the life of the device. If a breakdown is detected, most often the regulator is completely replaced with a new one. The main types of faults of this unit are:
- sagging or breakage of the working regulator spring;
- depressurization of the housing;
- mechanical wear of contact surfaces;
- corrosion of various surfaces;
- channel contamination.
Direct malfunctions can manifest themselves in three formats:
- jamming - the regulator does not operate every time it is needed, but periodically;
- incomplete closure - fuel is constantly drained into the tank (return line), regardless of pressure;
- jamming in the closed position - fuel does not drain under any parameters.
Signs of a malfunctioning fuel regulator have much in common with fuel pump failures and dirty filters. Thus, preliminary diagnosis can be made based on the following observations:
- Unstable operation and engine stopping in idle mode.
- Increased fuel consumption.
- Reduced motor power.
- Slow response to pressing the throttle pedal.
- Lack of smooth movement when accelerating the car, jerking is observed.
- The content of harmful components CO and CH in the exhaust increases significantly.
- The car does not accelerate.
The quality of the fuel has a significant impact on the service life of the fuel pressure regulator. You should also not neglect the timely replacement of fuel filters. Particular attention should be paid to the fuel regulator if the car has not been in use for a long time.
Causes of malfunctions
There are not many reasons why the fuel regulator fails. The element cannot be called ultra-reliable; it works, as they say, under wear and tear, and is very dependent on the quality of the fuel.
Causes of breakdowns:
- Marriage. This is not a common reason, but sometimes you come across defective products from domestic automakers. It is recommended to check the spare part before purchasing.
- Wear. Usually observed after 100-200 thousand kilometers. In the regulator, the membrane becomes less elastic, the pressure control valve gets stuck, and the spring becomes weaker.
- Bad fuel. Gasoline and diesel car engine fuel often contains too much moisture, debris, and foreign toxins. Water in fuel causes rusting of the metal parts of the regulator. Increasing over time, they interfere with its normal functioning and lead to weakening of the spring.
- The fuel filter is clogged. Garbage fractions in the fuel clog the system, including the RTD, and become clogged. This leads to spring wear and valve jamming.
On a note!
RTDs are usually not repaired, but replaced with a new one. But, if the cause of the breakdown is clogging, it can be cleaned.
How to check the fuel rail? Checking the RTD yourself
Checking the fuel pressure regulator is carried out to identify malfunctions or for prevention. Such checks are carried out based on the recommendations of the car manufacturer. But still, how to check the pressure in the fuel rail? Basically, the check consists of inspecting and checking the pressure of the fuel system at various engine speeds. Then comparisons are made with indicators that correspond to the norm.
It is necessary to carefully inspect the tightness of the connections, the condition of the vacuum hose, as well as the regulator itself. If no damage or defects are found, then the regulator is dismantled by completely disassembling it. If a blockage is detected in this unit, it is washed.
Important: the pressure in the fuel rail should be diagnosed using a pressure gauge. It is connected to a special diagnostic fitting.
How to check the fuel pressure regulator. Diagnostic tools regulate fuel pressure
You can also check the regulator yourself. To do this, you do not need to use any special tools or have any special auto mechanic skills. You will need to pinch or disconnect the valve and observe the force of the jet. Or for a better check, use a pressure gauge.
To measure the RTD pressure in the engine when turning on idle speed, it is worth connecting a pressure gauge, installing it between the fuel hose and the fitting. Don't forget to disconnect the vacuum hose. Below we will look at what pressure should be in the fuel rail of a VAZ 2110.
How do malfunctions of the fuel pressure regulator affect engine performance?
A faulty regulator valve affects not only operation, but also the very start of the engine. If the device is working properly, the pressure in the fuel rail does not drop after the engine stops. If the valve has a malfunction, then the pressure in the fuel rail drops when the engine stops. The engine will not start until the sediment has completely filled the system. And only after reaching the desired level, the first engine start signals may appear. Here everything will depend on the power of the battery. Otherwise, the engine will not be able to start. Therefore, if the pressure in the fuel rail does not hold, this indicates a malfunction!
In addition to the above, gas failures may occur during acceleration of the car, unstable idling, and a general weakening of engine power will begin to appear.
When should measurements be taken?
The operation of the power system is structured as follows:
- An electric fuel pump located in the tank pumps fuel along the line into the fuel rail and further to the injectors.
- The regulator limits the gasoline pressure at a certain level, releasing excess into the tank through the return pipeline.
- The injector mixes fuel with air, then the mixture is directed to the nozzles, which open at the command of the controller.
When the wear of the regulator (abbreviated as RTD), pump or injectors reaches a critical level, the pressure in the gasoline circuit will change towards a decrease or increase. There are 2 possible scenarios: there is not enough fuel mixture for normal engine operation, or there is an excess of it - the spark plugs are literally flooded with fuel.
In both cases, checking the pressure in the fuel rail located next to the cylinder head will help identify the problem. The element is a manifold with branches for injectors, to which the main gasoline line is connected.
The fuel pressure in the manifold should be measured if the following symptoms occur:
- the car accelerates poorly, after sharply pressing the accelerator pedal, jerking and deceleration are felt;
- the engine of a loaded car “does not pull” and starts poorly when cold;
- shots are periodically heard in the exhaust manifold;
- a warm engine does not start after a short period of parking (especially in summer); the starter needs to be turned for 20–40 seconds.
The first two signs indicate a clear lack of gasoline, resulting from a drop in pressure in the ramp. The third case is unburnt fuel entering the exhaust manifold with subsequent combustion (a popping sound is heard). The fourth symptom indicates leaking injectors when the cylinders are filled with pure gasoline during parking. Until the pistons release excess fuel, the engine will not start.
We recommend: When is it necessary to replace the oil pan gasket of a car engine?
Replacing the fuel pressure regulator in az 21 10 (and other cars)
To ensure that your car is always on the road and there are no problems with the fuel pressure regulator, you need to take the time for a thorough inspection.
1) Under the hood of the car, open the fitting plug, which is responsible for controlling the fuel pressure at the end.
2) Take a special protective metal cap and carefully unscrew the spool from the inner cavity of the fitting.
3) Then attach a hose with a pressure gauge to it. Secure it to the fitting using a clamp. After this, you should start the engine and check the pressure shown by the pressure gauge. It should not be higher than 325 kPa ( 3.25 Bar ).
4) Carefully disconnect the vacuum hose from the pressure regulator. You will immediately see how the pressure will increase on the pressure gauge. If this does not happen, you should replace the device with a new one. A device that has not been repaired cannot be repaired. But how to change the fuel pressure regulator?!
5) Now you can slightly reduce the pressure in the power system and remove the vacuum hose from the RTD. To do this, you will need to unscrew the reinforcing nut on the fuel drain pipes to the pressure regulator.
6) You need to unscrew the two bolts securing the device to the fuel rail.
7) Now you can remove the regulator from the fuel drain pipe itself. If the ring does not immediately detach and remains in the ramp, remove it. It is put on the regulator before installation. The regulator must be installed in the reverse order, observing the exact sequence.
So now you know the causes of fuel pressure regulator failure and how to replace the fuel pressure regulator. The most important thing is not to rush, and follow the sequence of actions.
Fuel pressure regulator (FPR) is part of the system that supplies the injection engine. This element maintains the fuel pressure in the injectors under various operating modes of the internal combustion engine. The regulator actually plays the role of a diaphragm valve, ensuring good performance and stable operation of the injectors and motor. It is important to know how the pressure sensor works and the signs that indicate its malfunction.
Purpose of the regulator
The sensor maintains the optimal pressure in the fuel rail, necessary for the correct operation of the injectors in different operating modes of the unit. The RTD determines the intensity of fuel supply and its quantity. Fuel enters the engine cylinders through the injectors.
Dosing accuracy and maintaining the required pressure is ensured by a membrane control valve, onto which springs press at one end and fuel at the other. There are two options for placing an element:
- The RTD is used in power systems with a check valve and is mounted on the fuel rail.
- In designs without “return”, the sensor is installed on the fuel tank.
In the first case, the fuel pump pumps fuel through the line from the tank. The resulting pressure affects the regulator. The device contains two chambers: fuel and spring, which are delimited by a membrane.
Location in the vehicle structure
In modern cars, two layouts of the fuel pressure regulator are used. In systems with a return line, it is installed on the fuel rail, and in designs without a “return” - directly inside the fuel tank (in the pump). The diagram located on the fuel rail involves connecting the regulator to two lines of the system:
Layout of the fuel pressure regulator in the system
- inlet - the supply channel from the fuel tank to the power system;
- return exhaust – channel for draining excess fuel (pressure relief).
In such a system, when the regulator opens, excess fuel enters the return line and then into the fuel tank. This scheme has some disadvantages:
- complexity of the design and the need to install an additional pipeline;
- heating of excess fuel when it enters the ramp, which increases the vapors generated in the tank.
Each fuel regulator has its own factory settings and is suitable for a given car model. There are also universal designs for injection systems, which are equipped with pressure gauges and the ability to manually adjust. They are installed instead of the standard regulator exclusively in the fuel rail.
When the fuel pressure regulator is placed directly in the tank, the required amount of working fluid with a given compression level immediately enters the engine without the use of an additional line. In this case, the excess is also discharged directly into the tank, but it does not enter the engine compartment, which eliminates its heating.
In this case, a constant pressure difference is established relative to atmospheric pressure, and the amount of vacuum in the intake manifold is taken into account by changing the injection duration.
Possible faults
Failures in the power system can occur for various reasons. Therefore, when diagnosing, you need to take into account some features of a regulator failure and symptoms of low fuel pressure. The main features include:
- reduced power, high fuel costs;
- dips and jerks during acceleration and throttle change;
- unstable operation and engine shutdown at idle;
- slow car response when adding gas;
- The car does not pick up speed and does not accelerate.
Signs of low pressure in the RTD on gasoline cars are similar to symptoms of a malfunction in the fuel pump or a broken fuel filter. The system stops working correctly due to loss of spring force. In this case, the fuel does not reach the required level and goes into the check valve. As a result, the engine does not have enough fuel to accelerate and increase speed. Low pressure in the sensor reduces engine power. The electronic control system cannot optimally adjust the fuel for different modes.
Another cause of failure could be a clogged RTD or reduced throughput.
In this case, the engine stalls in any operating mode. A clogged regulator can lead to an excessive increase in pressure and fuel overflow through the connections of the sealing elements.
The fuel pump always takes in fuel with some reserve to prevent a possible decrease in the performance of the injectors and sensor. Therefore, if it is difficult to drain fuel into the return valve, the pressure in the system increases.
Periodic jamming of the pressure regulator also leads to failures.
The car begins to move jerkily, pressure drops occur in the sensor. The cause of the breakdown may also be wear of the valve inside the device. Its service life can be shortened by low-quality fuel with impurities, or by keeping the machine idle for a long time without starting the engine.
Checking an element
In most cases, if problems are detected, it is better to completely replace the fuel pressure regulator. Changing individual elements, cleaning and other manipulations cannot always restore the required performance to the device. The affordable price of the RTD also contributes to the decision to completely replace the component.
The easiest, most accessible and effective way to check the regulator is to measure the indicators using a tire pressure gauge. To determine the idle pressure, the device is connected between the fitting and the fuel system hose. The measurements must indicate pressure within a certain range. The vacuum hose is then disconnected.
As the pressure increases, the indicator should be between 0.3−0.7 Bar. If the value is outside this range, install a new vacuum hose and repeat the test in the following order:
- The fuel pressure on the end area of the ramp is determined after unscrewing the fitting plug. It is also necessary to check the O-ring for integrity and elasticity. If there are defects, then the element or the entire plug must be replaced.
- The umbrella is unscrewed from the fitting; for this you can use a metal valve cap. A hose with a pressure gauge is connected to the part and secured with clamps. After this, the engine is started and measurements are taken. Indicators within the normal range are 2.9−3.3 kgf per square meter. cm.
- The hose is disconnected from the regulator. You need to check the pressure gauge readings; the pressure should increase to 20−70 kPa. If the value remains low or zero, the device must be replaced.