Dimensions of wheel bolts Moskvich 2141
For model 2141, the wheel is attached to the hub using wheel bolts. The number of fasteners depends on the year of manufacture of the model and is presented in the table below.
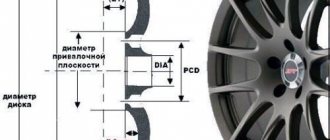
General fastener dimensions:
- Number of fastening elements: -;
- Fastener size: M14x1.5;
- Mounting hole diameter (PCD): -;
- Disc offset (ET): -.
Important: the data presented above are the limits of values for all modifications of the car; specific figures depend on the year of manufacture.
Rules for selecting wheel fasteners:
For cast and stamped wheels, different wheel fasteners are often used - this applies to the length of the bolts, since the thickness of different types of wheels can vary significantly.
When selecting any fastener, special attention should be paid to the thread pitch. This parameter is always indicated in the marking after the “x” sign.
Most wheel fasteners have metric fine pitch threads (M12x1.25/M12x1.5/M14x1.25/M14x1.5), which should match the threads of the studs or tapped holes in the wheel hub.
Important: the marking of the M12x1.5 mounting bolt is deciphered as follows: thread with a nominal diameter of 12 (mm), thread pitch 1.5 (mm).
Other names:
In European countries, the Soviet and Russian passenger car of the third group of the small class Moskvich 2141 was sold under the name ALEKO. From 1998 to 2002, a modernized version of the Moskvich 2141-02 (-45, −00, −22, −23, −24, −25) was produced, known under the name Svyatogor.
Years of production Years of production of all modifications of the model: 1986 - 2002.
Dimensions of wheel nuts Moskvich 2140
For model 2140, the wheel is attached to the hub using wheel nuts. The number of fasteners depends on the year of manufacture of the model and is presented in the table below.
General fastener dimensions:
- Number of fastening elements: -;
- Fastener size: M12x1.5;
- Mounting hole diameter (PCD): -;
- Disc offset (ET): -.
Important: the data presented above are the limits of values for all modifications of the car; specific figures depend on the year of manufacture.
Rules for selecting wheel fasteners:
For cast and stamped wheels, different wheel fasteners are often used - this applies to the length of the bolts, since the thickness of different types of wheels can vary significantly.
When selecting any fastener, special attention should be paid to the thread pitch. This parameter is always indicated in the marking after the “x” sign.
Most wheel fasteners have metric fine pitch threads (M12x1.25/M12x1.5/M14x1.25/M14x1.5), which should match the threads of the studs or tapped holes in the wheel hub.
Important: the marking of the M12x1.5 mounting bolt is deciphered as follows: thread with a nominal diameter of 12 (mm), thread pitch 1.5 (mm).
Other names:
The small class III group car Moskvich 2140 also has alternative names Moskvich 1500 and Moskvich 1500.
Years of production period: 1976 – 1988.
Other parameters of Moskvich 2141:
| General parameters of Moskvich 2141 wheel bolts | |||
| General view General view of wheel bolts | Quantity (units) Number of fasteners per hub for Moskvich 2141. | ||
| Dimensions (mm) Metric Fastener Size: Thread M14 x 1.5 means: M14 – thread diameter 14 (mm); 1.5 — thread pitch (distance between adjacent threads). | General form Wheel mounting type: To fasten wheels or disks, 2 main types of fasteners are used: - wheel bolts; -wheel nuts. | ||
| (bolt drawing) | — | M14x1.5 | Bolt |
| Wheel bolt size tables Moskvich 2141 | ||||
| Year | Quantity (units) Number of fasteners per hub for Moskvich 2141. | |||
Caution: the above data are the official figures of the manufacturer, however, please note that the information is for reference only and does not guarantee absolute accuracy.
Other parameters of Moskvich 2140:
| General parameters of Moskvich 2140 wheel nuts | |||
| General view General view of wheel bolts | Quantity (units) Number of fasteners per hub for Moskvich 2140. | ||
| Dimensions (mm) Metric Fastener Size: Thread M14 x 1.5 means: M14 – thread diameter 14 (mm); 1.5 – thread pitch (distance between adjacent threads). | General form Wheel mounting type: To fasten wheels or disks, 2 main types of fasteners are used: - wheel bolts; -wheel nuts. | ||
| (drawing of nuts) | – | M12x1.5 | screw |
| Wheel nut size tables Moskvich 2140 | ||||
| Year | Quantity (units) Number of fasteners per hub for Moskvich 2140. | |||
Caution: the above data are the official figures of the manufacturer, however, please note that the information is for reference only and does not guarantee absolute accuracy.
Source: razmery.info
Replacing original wheels Moskvich-2141
Many owners are thinking about replacing standard Moskvich-2141 wheels with models from other cars or completely new ones. And the reason here is not only the desire to tune your car, but also the difficulties in finding “original” parts. And in markets and stores today they offer a wide range of products, both new and used, both steel and light alloy. But you need to figure out what kind of wheels can be installed on the Moskvich-2141 so that there is no harm to traffic safety.
The manufacturer gave the following recommendations regarding wheels for Moskvich-2141 . Tire sizes are 165/80 R14, 175/70R14, 185/70R14 and 185/65R14. In this case, steel wheels must have a 5J rim with an ET offset of 45 mm. A 5.5J rim with a 42mm offset is also allowed. Alloy wheels for Moskvich-2141 must have a 5.5J rim and an offset of 37 mm or a 6J rim and an offset of 33 mm. Note that the plant also allows the installation of tires 175/65 R15, as well as 185/65R15. In this case, the wheels must be 5.5J or 6J, and the offset must be 42 mm. It is worth paying attention to one nuance. If wheels are installed on a Moskvich-2141 with a profile width of 185 mm, such a wheel may not be mounted in the “original” fastener for the “spare tire” or in the niche for it.
In addition to the parameters described above, when selecting wheels for Moskvich-2141, mounting holes are also a decisive factor. This machine has 4 mounting holes with a circumference of 108 mm. In addition, it is important that the diameter of the central hole of the wheel rim is about 1-2 mm larger than the diameter of the hub. For the AZLK-2141 car, the latter is 52 mm.
If we talk about the selection of wheels for Moskvich-2141 from foreign cars, then here you can make a whole list of models. It will include Alfa Romeo 75 7th generation, Audi 80, 90, 100 until 1991, Ford Escort, Taunus, Cortina, Scorpio after 1995, Mondeo 1996-2000, Focus 1st generation, Cougar, Fiesta 3, 5 generations, as well as 4 generations until September 2008. In addition, wheels from many models of Peugeot and Citroen, SAAB 9000 1988-1992, Kia Alegro, Porsche 924 are suitable. Naturally, when selecting wheels for Moskvich-2141 , you may encounter the problem of discrepancy between the diameters of bolt or hub holes. The first ones can be drilled out if necessary. If they are more than required, then it is better to refuse such a purchase. In the case of hub holes, if it is larger on the disk than the diameter of the hub, then this is not critical. If it is less, then in this case it is also better not to purchase such disks.
Note that many tuning enthusiasts install wheels on Moskvich-2141 with a larger diameter and with different characteristics than those recommended by the factory. The main problem in this case is that the edge of the rubber does not reach the spring cup of the shock absorber strut of the front wheels, which is the element closest to the wheel. In such cases, replacing the rack with a unit from Moskvich Ivan Kalita can help.
Answers (2)
Moskvich 2141 was equipped with 14-inch wheels with tires measuring 165 / 80 / R14.
Wheel parameters: bolt pattern - 4x108, width 5J, offset - ET 45 mm
Wheel parameters: bolt pattern - 4x108, Pejo 206 Ford focus Ford fiesta
Discs
Tracing its pedigree from Opel, the Moskvich model 400/401 was equipped with narrow 4.50-16 or 5.00-16 tires. Today, such “shoes” are of interest only to restorers. However, it was radically different from other cars of those years in the design of its wheels: the cast-iron brake drum simultaneously served as both the hub and the wheel disk, and the mounting studs were spaced apart to the maximum possible diameter. Therefore, the wheel was actually devoid of a hub and consisted only of a rim with sockets for fastening nuts. The entire structure was covered with a convex chrome cap.
Starting with the 402 model, there was a transition to a smaller diameter, and the seat of the wheel on the hub did not subsequently change for Muscovites until the advent of the front-wheel drive model 2141! This means that “theoretically” any wheel from any rear-wheel drive Moskvich starting from 402 can be installed on any Moskvich up to the late 2140. In practice, a disc brake caliper will prevent this.
In the photo: Moskvich-400 (1, 2), -402, -403 and -410
True, the rim of models 402, 403, 407 and 410 had a diameter of 15 inches, and on later models (408, 412, 2140, etc.) a 13-inch one was used - according to the fashion of that time, the outer diameter of the disk (and tire ) gradually decreased, and the profile width, on the contrary, increased. An interesting point: wheel rims for Muscovites were produced by two factories - GAZ and VAZ, and the wheel with an asymmetrical rim profile for Muscovites, produced at VAZ, differs from the corresponding part for Zhiguli only in the number of holes for bolts and the shape of the hub stamp, and the rim itself is exactly the same!
In the photo: Moskvich-402 and Moskvich-2140
Until 1970, 4J-13 wheels were installed on sedans, and rims increased to 4 ½ inches in width were used on station wagons and vans. After 1970, all cars were equipped with wider wheels. Disks with a symmetrical rim produced by GAZ can be easily distinguished by four ventilation windows, and since 1973, new disks with an asymmetrical rim profile and six oval ventilation holes began to be installed on all Muscovites. In 1980-1981, wheels of the same type, but with a rim width of 5J, were produced by the GAZ plant. Discs with symmetrical rims can only be used on Moskvich vehicles with drum brakes on all wheels.
Tires and wheels in Tyumen
There are cone springs and a cup of reduced diameter. You can also upgrade the standard racks. Instead of the cut-off “original” cup, a part from the rear shock absorber of the VAZ-2109 is welded. Springs are selected according to the size and stiffness of the foreign car. But still, it is better to limit the scope of wheel selection to the framework established by the manufacturer.
Finally, we note that when choosing wheels for Moskvich-2141, it is not recommended to experiment with offset. As it increases, the load on the hub bearings increases several times. In addition, the retracement arm changes. This can provoke completely unpredictable changes in the car's handling. Therefore, the disc offset characteristics for Moskvich-2141 should be close to the values specified by the factory.
Site search
In my opinion, a huge amount of material has already been written about the installation of various kinds of non-original wheels on Moskvich 412 series. However, there are often still rather contradictory information regarding which wheels can be adapted for installation on a Moskvich, and for which it is inappropriate to do this... It must be remembered that installing non-original (non-certified for it) wheels on a car is illegal, and , to be fair, really unsafe. Therefore, if you really feel itchy (as, for example, I
) install other wheels, you need to at least approach such tuning responsibly.
I had three reasons for installing non-original wheels: 1. Potentially better characteristics of larger wheels (both in width and diameter) in terms of smoothness and directional stability. 2. Larger wheel diameter, which affects the speed characteristics of the car. 3. Appearance.
The last two motives are purely subjective and personally important to me. The choice initially settled on 14-inch wheels. I initially did not seriously consider the options for 15-inch wheels, because I think that this is too large a size for use on a Moskvich.
So, as you know, standard wheels have the following parameters: landing diameter - 13 inches rim flange width - 5 inches rim shape code - J number of studs x diameter on which they are located - 5 x 115mm offset - 30mm hub hole diameter - 74mm
The task, therefore, was to find the wheels that were closest in parameters, differing only in the landing diameter - 14 inches. The wheel options for Mercedes and BMW cars (including the ''15'' ones) are no longer available, since they have stud diameters of 112 and 120 mm, respectively (at least for the common models known to me). You cannot install such wheels on Moskvich. A variant of wheels from Mazda 626, Xedox 6, Toyota HiAce, Toyota Picnic, etc. has appeared. One of the variants of wheel rims used on these cars has the following parameters:
landing diameter - 14 inches rim flange width - 6 inches rim shape code - J number of studs x diameter on which they are located - 5 x 114.3mm offset - 38mm hub hole diameter - 67mm
There are both stamped steel and light alloy wheels. In addition, they are common enough that they can be easily found for sale. The diameter of the pins is close enough to the original one (the offset of the pins relative to the holes is 0.35mm) so that the difference can be neglected. However, when tightening the nuts, you need to pay attention to the alignment of the wheel. It turned out that the offset of the new wheels was too large, so that the front wheels hit the inside of the upper control arm, and the rear wheels hit the inside of the wheel arch during turns and when the car rolls. Therefore, it turned out to be necessary to order new studs extended by 15 mm (all 20 pieces), and to make spacers for the wheels that increase the track.
A resident of Odessa, known as Uncle Vova, created a unique car - Moskvich-2141, capable of overtaking foreign cars like the BMW M4, Porsche Cayenne and Audi S3! And what’s most interesting is that Uncle Vova left the original engine - reinforced connecting rods, liners and pistons were installed in the engine, and the main feature was a turbine. Moskvich got the transmission and rear suspension from the Audi S6. The power of the improved Moskvich remains a mystery, but there are suggestions that the car can develop 300-350 horsepower.
Comments:
Nyakoy si
Moskvich is power!
GOST
Well, yes, in Monte Carlo, as I see it, everyone drives such Muscovites
Ukraintsite
Ukrainians are the same Russians, only more capable!
CL500
In my opinion, this is all somewhat exaggerated, it’s just that young people are dragging after their enthusiastic grandfather, 400 horsepower or a little less is not enough for Moskvich to compete with the M4 or S3, he needs much more, if only because he has an ancient and unsportsmanlike transmission - no sport modes, settings, etc. A separate issue is tires and weight distribution...
Onya from the horse
For 45 years now, Russia has been oppressing Bulgaria - our media, under the dictation of Russia, are constantly promoting how practical, inventive and resourceful the Russian people are, how with a light and condescending smile he puts Western engineers and inventors with their heads in the clouds in their place. Here was the Iron Curtain, which did not allow us to check whether the West was really as bad as it was described... their “good” is as simple as possible, they do not pay attention to anything beyond the minimum! In general, there is now some kind of mania in Russia to introduce Western engines, chassis and transmissions into their tins and call this real competition for Western cars. And all this with one goal - to amuse the self-esteem of the average person, to inspire him that “we also gave something to the world.” This Uncle Vova is a resident of a Ukrainian city, but he is Russian to the core; in the video he speaks not Ukrainian, but Russian! They say about such a shameless hybrid war and assimilation policy: “The wolf changes its skin, but not its nature.”
Rusnak
To Onya’s comment from the horse: Uncle Vova is from Odessa, and in Odessa everyone speaks Russian. And most of the population of Ukraine considers themselves Russians, not Ukrainians. What kind of hybrid wars do you imagine...
Klassiker 05/08/2021 Fakti.bg 03/13/2021
GOST
Looking at the comments, I really believe that when choosing between BMW and Moskvich, you will really choose Moskvich. Who knows, maybe you really think so, just imagine what will happen if you actually compete with the M4. Only with an impartial assessment, and not with the nationalistic destruction of complexes
Alex
This engine cannot be equipped with an 8 valve cylinder head. Surely it was changed. The transmission is from Audi, and from the S6. The cabin is hardly designed to handle that kind of power, given the vibrations of the passenger seat under acceleration. I would rather put an Audi S6 8mac and add 2 turbines there. But this will be different.
InoSMI materials contain assessments exclusively of foreign media and do not reflect the position of the InoSMI editorial staff.
Wheel size for AZLK 2141 Svyatogor
You need to move the wheels outward at least 10-12mm to avoid all problems. For the spacers I used 4mm thick aluminum sheets. There were three spacers for each wheel. The new wheel hub holes are too small to fit onto the front suspension hubs. I had to expand them in diameter by approximately 7-8mm with a grinder - to the required 75mm. After all these alterations, you can drive on new wheels, in my opinion, quite safely. By the way, in the photo in the front I have wheels from a Toyota Picnic, and in the back from a Mazda 626. They are very similar in appearance, but slightly different (the first have 14 slots in the disk, the second have 15). This is by the way.
I used the common tire size 185/65R14. At the same time, the rolling diameter increased by approximately 4% compared to 175/70R13 tires; accordingly, the vehicle speed at a given engine speed increased by the same amount, and accordingly, the acceleration dynamics in a given gear worsened. Subjectively, the ride quality and directional stability have improved significantly. I did not control fuel consumption, but other things being equal (speed, tire pressure, temperature, tread pattern, etc.) it can increase slightly due to an increase in tread width. In my opinion, there are no other factors influencing consumption with new wheels. Please write with suggestions and criticism to [email protected]
Selection of rims for Moskvich 2141
However, popular modern cars are not equipped with wheels of this size. The closest to these indicators are common disks with a PCD of 114.3 mm. Japanese and Korean cars are equipped with such wheels, for example, some Mazda, Mitsubishi, Hyundai models.
The existing difference of 0.7 mm in the diameter of the circle where the fastening bolts are located can be neglected, since each hole is shifted relative to the center by 0.35 mm, which is compensated by the conical fit of the fastening nuts. If the wheel offset is greater - for example, 35 mm, it turns out to be recessed 5 mm into the “depth” of the arches, due to which the low “Moskvich” cutouts (at the rear) do not interfere with the normal rotation of the wheels. It is not recommended to use wider tires, since in this case the gap between the rear wheel and the spring on one side, and the wing on the other, will be unacceptably small. However, finding wheels less than 5.5 inches wide will not be easy, since five-stud hubs today are only equipped with heavy and powerful cars, which are not equipped with narrow wheels.
When purchasing and installing “castings” on “Moskvich” models 412 and 2140, you should take into account that such disks, as a rule, have a large thickness in the mounting plane, so the length of the standard studs may not be enough and you will have to order extended ones from turners. In this case, the operation of fastening the disk should be treated more responsibly, strictly observing the sequence of tightening the nuts according to the “star” pattern. Discs with cylindrical rather than tapered holes may work without stud extensions because their special extended nuts allow them to "grab" the threads deep into the disc. However, their use in this case is undesirable - problems with wheel alignment may arise.
Finally, you need to pay attention to the diameter of the hole for the hub in the disk - the DIA parameter. For “native” Moskvich wheels it is 74 mm, and for many alloy wheels it is less.
As a last resort, in order to seat the disc on the thickened part of the hub, you can chamfer the inside of the hole on the mating plane of the disc or bore the central hole on a machine.
Related articles:
OverviewCharacteristics The AZLK-2335 Moskvich passenger pickup truck was created in the early 1990s. Based on...
There is a lot of junk from the 41st, mainly interior elements and electrical equipment, if anyone needs anything...
VAZ-2106 engine The VAZ-2106 engine was developed by the Volzhsky Automobile Plant based on the VAZ-2103 power unit for the new…
Tuning Moskvich 412: car transformation Tuning the Moskvich carMoskvich tuning appeared quite a long time ago, back in the days...
Drilling disks on Moskvich 412
#1 another
- Users
- 1125 messages
- Gender: Male
- City: Kishmishnev
- Top
#2 965
- City: USSR, Moscow
Moskvich's native seat size: 5 x 115
Also suitable size 5 x 114.3
- Top
#3 One
- Gender: Male
- City: Moscow->Chertanovo Butovo
- Interests: auto, tourism
Moskvich's native seat size: 5 x 115
Also suitable size 5 x 114.3
- Top
#4 another
- Gender: Male
- City: Kishmishnev
Japanese size
- Top
#5 One
- Gender: Male
- City: Moscow->Chertanovo Butovo
- Interests: auto, tourism
- Top
#6 another
- Gender: Male
- City: Kishmishnev
- -1
- Top
#7 [email protected]
- Gender: Male
- Moscow city
can you give a couple of examples of car models?
- Top
#8 RINICH
- Gender: Male
- City: St. Petersburg
- Interests: DIY, modeling, design, non-standard solutions to technical issues
- Top
#9 another
- Gender: Male
- City: Kishmishnev
- Top
#10 One
- Gender: Male
- City: Moscow->Chertanovo Butovo
- Interests: auto, tourism
They won't fit from a Merc, they will fit on stiletto heels, but only to tighten them. At one time I already tried to fit myself into an Izh combi. the rims broke off, but I installed the steering wheel
- Top
#11 another
- Gender: Male
- City: Kishmishnev
Mercedes has 5x112 like the Fvaudishkodaseat =)
Wheels of the Land of Soviets: what Muscovites wore
Discs
Tracing its pedigree from Opel, the Moskvich model 400/401 was equipped with narrow 4.50-16 or 5.00-16 tires. Today, such “shoes” are of interest only to restorers. However, it was radically different from other cars of those years in the design of its wheels: the cast-iron brake drum simultaneously served as both the hub and the wheel disk, and the mounting studs were spaced apart to the maximum possible diameter. Therefore, the wheel was actually devoid of a hub and consisted only of a rim with sockets for fastening nuts. The entire structure was covered with a convex chrome cap.
Starting with the 402 model, there was a transition to a smaller diameter, and the seat of the wheel on the hub did not subsequently change for Muscovites until the advent of the front-wheel drive model 2141! This means that “theoretically” any wheel from any rear-wheel drive Moskvich starting from 402 can be installed on any Moskvich up to the late 2140. In practice, a disc brake caliper will prevent this.
In the photo: Moskvich-400 (1, 2), -402, -403 and -410
True, the rim of models 402, 403, 407 and 410 had a diameter of 15 inches, and on later models (408, 412, 2140, etc.) a 13-inch one was used - according to the fashion of that time, the outer diameter of the disk (and tire ) gradually decreased, and the profile width, on the contrary, increased. An interesting point: wheel rims for Muscovites were produced by two factories - GAZ and VAZ, and the wheel with an asymmetrical rim profile for Muscovites, produced at VAZ, differs from the corresponding part for Zhiguli only in the number of holes for bolts and the shape of the hub stamp, and the rim itself is exactly the same!
In the photo: Moskvich-402 and Moskvich-2140
Until 1970, 4J-13 wheels were installed on sedans, and rims increased to 4 ½ inches in width were used on station wagons and vans. After 1970, all cars were equipped with wider wheels. Disks with a symmetrical rim produced by GAZ can be easily distinguished by four ventilation windows, and since 1973, new disks with an asymmetrical rim profile and six oval ventilation holes began to be installed on all Muscovites. In 1980-1981, wheels of the same type, but with a rim width of 5J, were produced by the GAZ plant. Discs with symmetrical rims can only be used on Moskvich vehicles with drum brakes on all wheels.
Since 1982, Moskvich wheels have been produced without three protrusions for attaching the wheel cap. Since the chrome part that covered the entire central part was eliminated, small caps appeared in the central hole instead; on the AZLK-2140 “Lux” model, the hub was covered with plastic caps, “fashionable” at that time, fastened with wheel nuts.
In the photo: Moskvich-2140
The front-wheel drive Moskvich model 2141 had its own wheels with original parameters. They differed in both the rim diameter (14 inches) and the number of mounting holes (four instead of five). In terms of the bolt-to-bolt distance (4 x 108 mm), the 5J wide wheels with an offset of 45 mm were identical to the Audi part.
In the photo: Moskvich-2141
Until 1960, Moskvich models 402 and 407 were equipped with M-45 tube tires size 5.60-15, which later became tubeless; The cars were also equipped with tires of the new M-57 and M-59 models.
It is interesting that in the mid-sixties, Muscovites were produced precisely with the “tubeless” tire that is relevant today, but already in the early seventies, they, like the newfangled Zhiguli, began to be equipped with tube wheels. The reason is simple - firstly, speeds increased, so there was a risk of the tire falling off the wheel rim. Secondly, a “tubeless” tire with a soft and low sidewall (which is what 13-inch tires became like) did not tolerate the road surface of that time well.
Until November 1965, the 408 rolled off the assembly line on M-107 tube tires with dimensions 6.00-13, and from November 1965 to 1970 on tubeless tires. The 423 station wagon and 433 van were equipped with “reinforced” M-100 tires with dimensions 6.40-13. It’s not worth putting these harsh “universal” tires on any Moskvich with a sedan body - they are heavier and tougher - this will not bring joy to either the car or its owner.
In the photo: Moskvich-408
Until 1970, the more powerful 412 was equipped with the same M-107 tires, but with additional markings indicating that the rubber was “high-speed,” that is, capable of withstanding prolonged driving at speeds over 120 km/h. At that time, such tires were really considered “high-speed” - it sounds a little funny, but if you remember that the 401st and Pobeda developed only about a hundred kilometers per hour, then the enthusiastic emotions of the drivers of the new products become more understandable.
In the photo: Moskvich-412
In 1970-1978, all Muscovites with a sedan body were produced with diagonal low-profile tube tires measuring 6.45-13 models M-130A and M-119A, and station wagons were equipped with high-profile tires model M-100. On the sidewall of some M-130A tires there was the inscription “prostor” - it is believed that this is rubber for export modifications.
In 1978, the place of outdated models was taken by the more modern “diagonal” M-145. This tire is a real long-liver: it was not only found in the original equipment of rear-wheel drive Moskviches until their production ceased, but is still (!) produced and available for sale! That is why most connoisseurs of stock rear-wheel drive vehicles with the AZLK emblem remain faithful to this model. However, the M-100 “truck” tire also lived a long conveyor life - from 1967, when it began to be installed on Moscow station wagons and vans, and until 2001 (!), when the Izhevsk “pie” model 2715 was discontinued.
But not just “diagonal”: in October 1980, Muscovites began switching to radial tires – steel cord MI-166. Until 1982, “universal” versions still ran on bias-ply tires of the M-145 model with dimensions 6.95-13. However, station wagons and versions for “rural areas” also had more original “shoes”: M-177 from 1978 to 1983 on the “collective farmer” 21406, M-179 on the station wagon 2137 from 1982 and radial tires M-183Ya on 21406 1984. Like the Zhiguli, in the mid-eighties, AZLK cars switched to an improved “radial” model MI-16 with a dimension of 165/80 R13.
That is why Muscovites owners were not spared all the delights of using radial tires, which could fail due to breaker deformation long before the tread wear limit. Alas, soft and “delicate” radial tires were simply not adapted to the realities of Soviet roads and the habits of drivers of those years. The “tire” variety provided various models of rear-wheel drive Moskvich vehicles with the required handling and stability characteristics - of course, in the warm season.
In the photo: Moskvich-426, -427, -434 and -2137
In Soviet times, “Muscovites” faced completely different problems, unknown to the modern motorist: I don’t care about fat – I wish I could live! In the sense that their cars ran on anything - on the most mind-boggling combinations of tires, on “weld-on”... As a result, a flat tire or the need to re-flare a tire during an ordinary trip was not considered something special.
Likewise, drivers of those years did not see a problem with slippery road surfaces on any tires. Of course, the speeds were completely different, but... To be fair, it should be noted that the cars of the Moscow Automobile Plant were able to drive, including fast - for example, if professional athletes were behind the wheel, and the wheels were not “shod” with the supposedly tenacious Soviet “radial” , but in real Dunlop or Goodyear.
The already mentioned 2141 stood out not only with its wheels, but also with its tires. Its 14-inch “custom” format tires had a fairly small width (165 mm) but a high profile (80%). By the way, this is exactly the wheel size (165/80 R14) that the first generation Renault Logan has. In addition to the MI-180 tube tires, the AZLK-2141 was equipped with M-229, BL-85 tires or even imported Goodyear GT-70 tires with a dimension of 175/70 R14.
Dimensions Moskvich 2141 2-01 1.5. Everything about the dimensions of the Moskvich 2141 car can be found in the RST catalog. Moskvich 2141 wheel size is 165/80 R14 S (tire and wheel size), size
What kind of bolt pattern for Moskvich 2141
Moskvich 2141 was equipped with 14-inch wheels with tires measuring 165 / 80 / R14.
Wheel parameters: bolt pattern - 4x108, width 5J, offset - ET 45 mm
Wheel parameters: bolt pattern - 4x108, Pejo 206 Ford focus Ford fiesta
Discs
Tracing its pedigree from Opel, the Moskvich model 400/401 was equipped with narrow 4.50-16 or 5.00-16 tires. Today, such “shoes” are of interest only to restorers. However, it was radically different from other cars of those years in the design of its wheels: the cast-iron brake drum simultaneously served as both the hub and the wheel disk, and the mounting studs were spaced apart to the maximum possible diameter. Therefore, the wheel was actually devoid of a hub and consisted only of a rim with sockets for fastening nuts. The entire structure was covered with a convex chrome cap.
Starting with the 402 model, there was a transition to a smaller diameter, and the seat of the wheel on the hub did not subsequently change for Muscovites until the advent of the front-wheel drive model 2141! This means that “theoretically” any wheel from any rear-wheel drive Moskvich starting from 402 can be installed on any Moskvich up to the late 2140. In practice, a disc brake caliper will prevent this.
In the photo: Moskvich-400 (1, 2), -402, -403 and -410
True, the rim of models 402, 403, 407 and 410 had a diameter of 15 inches, and on later models (408, 412, 2140, etc.) a 13-inch one was used - according to the fashion of that time, the outer diameter of the disk (and tire ) gradually decreased, and the profile width, on the contrary, increased. An interesting point: wheel rims for Muscovites were produced by two factories - GAZ and VAZ, and the wheel with an asymmetrical rim profile for Muscovites, produced at VAZ, differs from the corresponding part for Zhiguli only in the number of holes for bolts and the shape of the hub stamp, and the rim itself is exactly the same!
In the photo: Moskvich-402 and Moskvich-2140
Until 1970, 4J-13 wheels were installed on sedans, and rims increased to 4 ½ inches in width were used on station wagons and vans. After 1970, all cars were equipped with wider wheels. Disks with a symmetrical rim produced by GAZ can be easily distinguished by four ventilation windows, and since 1973, new disks with an asymmetrical rim profile and six oval ventilation holes began to be installed on all Muscovites. In 1980-1981, wheels of the same type, but with a rim width of 5J, were produced by the GAZ plant. Discs with symmetrical rims can only be used on Moskvich vehicles with drum brakes on all wheels.
Since 1982, Moskvich wheels have been produced without three protrusions for attaching the wheel cap. Since the chrome part that covered the entire central part was eliminated, small caps appeared in the central hole instead; on the AZLK-2140 “Lux” model, the hub was covered with plastic caps, “fashionable” at that time, fastened with wheel nuts.
In the photo: Moskvich-2140
The front-wheel drive Moskvich model 2141 had its own wheels with original parameters. They differed in both the rim diameter (14 inches) and the number of mounting holes (four instead of five). In terms of the bolt-to-bolt distance (4 x 108 mm), the 5J wide wheels with an offset of 45 mm were identical to the Audi part.
In the photo: Moskvich-2141
Until 1960, Moskvich models 402 and 407 were equipped with M-45 tube tires size 5.60-15, which later became tubeless; The cars were also equipped with tires of the new M-57 and M-59 models.
It is interesting that in the mid-sixties, Muscovites were produced precisely with the “tubeless” tire that is relevant today, but already in the early seventies, they, like the newfangled Zhiguli, began to be equipped with tube wheels. The reason is simple - firstly, speeds increased, so there was a risk of the tire falling off the wheel rim. Secondly, a “tubeless” tire with a soft and low sidewall (which is what 13-inch tires became like) did not tolerate the road surface of that time well.
Until November 1965, the 408 rolled off the assembly line on M-107 tube tires with dimensions 6.00-13, and from November 1965 to 1970 on tubeless tires. The 423 station wagon and 433 van were equipped with “reinforced” M-100 tires with dimensions 6.40-13. It’s not worth putting these harsh “universal” tires on any Moskvich with a sedan body - they are heavier and tougher - this will not bring joy to either the car or its owner.
In the photo: Moskvich-408
Until 1970, the more powerful 412 was equipped with the same M-107 tires, but with additional markings indicating that the rubber was “high-speed,” that is, capable of withstanding prolonged driving at speeds over 120 km/h. At that time, such tires were really considered “high-speed” - it sounds a little funny, but if you remember that the 401st and Pobeda developed only about a hundred kilometers per hour, then the enthusiastic emotions of the drivers of the new products become more understandable.
In the photo: Moskvich-412
In 1970-1978, all Muscovites with a sedan body were produced with diagonal low-profile tube tires measuring 6.45-13 models M-130A and M-119A, and station wagons were equipped with high-profile tires model M-100. On the sidewall of some M-130A tires there was the inscription “prostor” - it is believed that this is rubber for export modifications.
In 1978, the place of outdated models was taken by the more modern “diagonal” M-145. This tire is a real long-liver: it was not only found in the original equipment of rear-wheel drive Moskviches until their production ceased, but is still (!) produced and available for sale! That is why most connoisseurs of stock rear-wheel drive vehicles with the AZLK emblem remain faithful to this model. However, the M-100 “truck” tire also lived a long conveyor life - from 1967, when it began to be installed on Moscow station wagons and vans, and until 2001 (!), when the Izhevsk “pie” model 2715 was discontinued.
Moskvich 2141
| Dimensions (mm) Metric Fastener Size: ThreadM14 x 1.5 means: M14 – thread diameter 14 (mm); 1.5 — thread pitch (distance between adjacent threads). | PCD (mm) Diameter between fasteners: The diameter of the circle on which the mounting holes for Moskvich 2141 are located. | ET (mm) Disc offset: The distance between the vertical plane of symmetry of the wheel and the plane of application of the disc to the hub. | ||
| Bolt | ||||
| 1986 | x | M14x1.5 | x | x |
| 1987 | x | M14x1.5 | x | x |
| 1988 | x | M14x1.5 | x | x |
| 1989 | x | M14x1.5 | x | x |
| 1990 | x | M14x1.5 | x | x |
| 1991 | x | M14x1.5 | x | x |
| 1992 | x | M14x1.5 | x | x |
| 1993 | x | M14x1.5 | x | x |
| 1994 | x | M14x1.5 | x | x |
| 1995 | x | M14x1.5 | x | x |
| 1996 | x | M14x1.5 | x | x |
| 1997 | x | M14x1.5 | x | x |
| 1998 | x | M14x1.5 | x | x |
| Year of release | |
| Start of release of the modification | 1987 |
| Year of modification end | 1997 |
| Body | |
| Body type | Hatchback |
| Number of doors | 5 |
| Passenger seats + driver | 5 |
| Body length | 4350mm |
| Body width | 1690mm |
| Body height | 1400mm |
| Vehicle wheelbase | 2580mm |
| Front track | 1440mm |
| Rear track | 1420mm |
| Minimum trunk volume | 370l |
| Engine | |
| Engine location | Front, longitudinal |
| Engine capacity | 1478cm 3 |
| Engine power | 72 hp/5400 rpm |
| Torque | 106/3200 n*m |
| Fuel supply system | Carburetor |
| timing belt | OHC |
| Number and arrangement of cylinders | 4 (Inline) |
| Cylinder diameter | 82mm |
| Piston stroke | 70mm |
| Compression ratio | 9.5 |
| Number of valves | 8V |
| Type of fuel | AI92 |
| Transmission | |
| Drive unit | Front |
| Number of gears | 5 |
| Suspension | |
| Front suspension type | Helical spring |
| Rear suspension type | Helical spring |
| Brake system | |
| Front brakes | Disk |
| Rear brakes | Drums |
| ABS | There is |
| Steering | |
| Steering type | Gear |
| Operating data | |
| Maximum speed | 150km/h |
| Acceleration time | 18 |
| Fuel consumption Combined cycle | 7.9 |
| Fuel tank volume | 55 |
| Vehicle curb weight | 1065kg |
| Permissible gross weight | 1465kg |
| Tire size | 165/80 R14 S |