- home
- car battery
- …
This problem can manifest itself both in winter (cold) and summer (warm) periods of time, and it practically does not depend in any way on winter starts. What happens when starting or when the engine is already running, one of the battery terminals begins to heat up wildly, if you drop water on it, it will begin to steam. Why does this happen and how to deal with it, let's figure it out...
At the very beginning, I want to say that this malfunction can occur on different cars (the make and model does not matter), and often this can be the reason for the battery failure, and in a very short period of time.
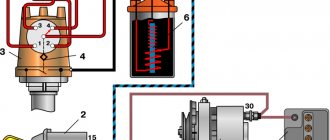
The positive terminal gets hot
Terminals are the current terminals for batteries. The vehicle's power supply wires are attached to them. They are made of lead.
If the positive contact on the battery heats up, this means that the wire has poor contact with the terminal. This may occur due to oxidation or due to water entering it.
Heating can cause ignition of wiring and a fire under the hood, melt insulation, and damage the battery case.
You can eliminate the causes of heating of the positive terminal as follows.
- Remove the end of the wire from the current terminal.
- Clean the contacts with sandpaper.
- It is advisable to change the wire that goes from the generator to the battery.
- Put the wire back on the terminal and sufficiently tighten the end of the wire that is connected to the current terminal on the battery.
To improve contact, it is necessary to select the desired ring diameter. Then the bolted connection will tightly grip the terminal and prevent this area from sparking and melting.
It is recommended to tighten the bolt nuts with two wrenches. This way you can avoid turning the bolt or nut.
If after cleaning the contacts a few days later a white oxide film of lead has formed again, which leads to poor contact between the wire and the battery, it is recommended to check the battery for electrolyte leakage. The battery may be deteriorating. Cracks have appeared on the battery body through which electrolyte vapors enter.
How to avoid problems
Here are some simple recommendations that will avoid oxidation of terminals and contacts and save your nerves and battery:
- Inspection and cleaning of terminals. Regularly monitor the condition of the terminals, remove oxides, and ensure that all contact connections are free of dirt and dust. If there is still dirt and oxides, clean it. A brush with metal bristles, emery cloth, and a cloth with gasoline will help you;
- Good contact. Check all contact connections. If there is a leak somewhere or a lot of overheating due to differences in materials, replace it. Also tighten the cleaned terminal clamp that is placed over the terminal tightly.
- Inspect the battery and wiring. If you regularly carry out the previous steps, but oxides appear again and overheating occurs, make sure that your battery is not damaged and that no electrolyte gets on the contacts. Also check the integrity of the wiring and replace damaged pieces of cable.
The negative terminal gets hot
If the negative terminal gets hot, it is due to poor contact with the body. The latter is used in the form of grounding. Oxidation as a result of the release of electrolyte vapors to the outside can also affect.
To eliminate the causes of heating of the negative terminal, it is recommended to do the following:
- Check whether both ends of the wire are connected well enough.
- Clean the terminal from oxides with sandpaper. If oxides still remain, replace the battery with a new one.
Heating of the ground wire from the battery is not in itself dangerous if it occurs due to a poor connection. In case of oxidation and gradual destruction of the battery, this is dangerous for the lives of other components of the car, to which the problem can spread. The heat may cause the body to melt, which will lead to sulfuric acid leaking into the inside of the car.
Briefly about terminals
The connection of the contact group of automotive electrical equipment with the battery terminals is made using metal terminals.
In accordance with international standards, the following types are produced:
- Type A. Designed for use in a European-made power supply. The leads are a truncated cone; the positive and negative current leads have a diameter of 19.5 mm and 17.9 mm, respectively.
- Type B. This is a contact for a vehicle power supply with element diameters of 11.1 mm for the negative and 12.7 mm for the positive terminal. Used in Japanese-made technology.
- Types F and G. Designed for connecting the on-board network cable to the battery using screws and bolts.
- Types T and E. They are used for power supplies made in Russia; they can also be used in European technology.
Batteries with terminals of type A and B have become widespread; many manufacturers produce equipment of the corresponding design. The terminals are metal clamps that are designed to ensure contact between the on-board network and the battery. To avoid poor contact, it is necessary to tighten the parts using bolts or screws passed through the body and secured with a nut on the other side.
Both terminals get hot
If both terminals heat up when starting the engine or when turning on the wipers, heated mirrors or seats, this means that the generator cannot cope with the load. Energy is additionally taken from the battery. In case of poor contact, these places become very hot.
To avoid overheating of both terminals when starting up or connecting additional devices, you must repeat all the steps that were described above separately for the negative and positive contacts.
Attention! When working with a battery, you must follow safety precautions and use rubber gloves. If the battery leaks, there is a possibility of damaging exposed skin on your hands.
Danger of heating battery terminals
An increase in the temperature of the contact group negatively affects the internal processes of the battery.
Frequent heating of the terminals leads to the following consequences:
- As the resistance at the contacts increases, the temperature of the internal plates of the battery may increase. With this phenomenon, the electrolyte begins to boil and evaporate rapidly. The source fails, the jars dry out, the internal plates crumble, and their own capacity decreases.
- Constant heating of the contacts leads to the appearance of cracks on the surface of the battery case. Electrolyte leakage will occur through the damaged areas, which threatens premature failure of the battery.
- At temperatures above the melting point of lead contacts, deformation of the leads and terminals occurs.
Sometimes overheating occurs when starting a vehicle. During engine operation, when a load is applied to the contact group, an increase in temperature is observed. In this case, the generator is unable to cope with the load, so the conductors begin to take the missing power from the battery.
If there is oxidation or damaged wires on the battery, the car owner may experience overheating.
If during the operation of the vehicle the starter jams and the generator does not start in a timely manner, it is necessary to control the power consumption of the on-board electrical equipment.
The wires coming from the battery get hot
It happens that the wire going to the charger gets hot. And the car owner thinks that this is a terminal.
The reasons for cable heating are as follows:
- small cable cross-section, which cannot withstand the load when connecting additional devices;
- break of several threads inside the cable;
- poor cable quality.
All this leads to the fact that the wires will heat up and may ignite. It is recommended to replace the cables with new and high-quality ones. Branded wires have passed European quality standards and have oil-, petrol- and heat-resistant insulation.
Important! It is best to connect the car battery terminals with a braided copper wire.
Why do the battery terminals get hot?
During operation of the electrical equipment of a vehicle, a malfunction may occur; the car owner notices that the positive terminal of the battery is heating up. Loss of normal contact at the power supply terminals occurs when exposed to external factors. It is necessary to prevent such influence on connections subject to high current loads and when operating in aggressive environments.
The generator is getting very hot – what should I do?
The problem with a car generator is one of the most common. And why should we be surprised? The operating conditions of the generator cannot initially be called favorable. During active use, the device gets exposed to oil, dirt, salt and various substances that have harmful effects. Their effect is aggravated by high temperatures occurring in the engine compartment.
Diode bridge of the Lada Priora generator
All automobile generating devices are united by their structural similarity. Regardless of the GI models, they are all susceptible to the same “diseases”, and, accordingly, methods for their “treatment”.
One of the most common problems with GU, along with increased noise and lack of charge, is its rapid heating.
It is worth a lot to be able to diagnose GI on your own. You should learn how to at least carry out initial diagnostics that would confirm the malfunction of the power unit.
Generator starter winding
Here is how it is recommended to check the device:
- Open the hood of the car;
- First of all, start checking the alternator belt.
The belt is checked for integrity and tension. If the material shows signs of wear, large cracks and fraying, then this is a reason for replacement. A bad belt puts extra stress on the generator and other vehicle systems. Excessive load on the generator means overheating and rapid failure of the unit.
As for tension, the situation is similar here. A weak or over-tightened belt will negatively affect the operation of the generator.
The second in line after the belt is the fuse located in the block. As a rule, it is provided by the car manufacturer.
Next, check for oxidation of the battery terminals and the wiring going to the power unit. It would be a good idea to check the connector of the generating device.
The methods described above will help determine whether the electrical connection of the unit is in order and whether the belt is intact. However, checking the device does not end there.
Here's what to do next:
- Turn on the ignition;
- Carefully monitor the battery charging indicator on the dashboard after starting the engine.
In general, if the indicator does not work when the ignition is on (half a turn of the key), then the battery may be dead, the indicator light itself may be damaged, or the wiring may be damaged. This may also indicate problems with the gene: failure of the tablet (voltage regulator), break in the winding or wear of the brushes.
If the indicator continues to light after starting the engine, then this also indicates a problem - one or more diodes of the generating device have failed, there is a short circuit in the circuit, the pulley is faulty, etc. The indicator light should not light up, since after starting, supplying consumers with current is entrusted not to the battery, but to the generator. A glowing indicator indicates that the battery continues to power electrical appliances.
Wiring
When it comes to overheating in the power supply system, why not pay attention to the wiring. In this case, it is recommended to test the entire positive cable laid from the battery to the power unit. It is possible that there is not enough insulation somewhere and there is a short circuit.
There should be a fuse on the wiring going from the battery to the main unit. When a diode bridge breakdown or other short circuit occurs, the fuse fails, not the positive wire. This option is available on some domestic models (for example, GAZ).
In any case, the car owner should look for the reason for the high voltage consumption. That's what the experts and electricians say. And the first thing they do is diagnose the battery.
As you know, during engine operation, the PG must provide a charge to the battery. If cans or something else fly off the battery, then the current flow process will be continuous and in large quantities, which will a priori cause the device to overheat.
| Cause | Solution | |
| Battery | High voltage consumption due to excessive current output, oxidation, short circuit and failure of cans | Replace battery, charge |
| Diode bridge | Lack of gasket, loose soldering, loose terminals, breakdown | Overhaul, replacement, repair |
| Bearings | Failure of the front, rear or both together | Replacement of wiring, new insulation |
| Wiring | Insufficient insulation, short circuit | Replacement of wiring, new insulation |
Diode bridge
Excessive heating of the generating device will certainly lead to further problems. Heating occurs for various reasons, but most often the diodes in the unit burn out.
In general, checking the diode bridge in such cases is a must. It happens that after overhauling the generating device or replacing machine components, the car service center forgets to put gaskets on. For example, under the rectifier unit itself. Because of this, the device begins to get very hot, as it short-circuits to the case without protection (gasket).
It could also be this: the soldering on the diode bridge is relaxing. The reason will only be revealed by opening the GU (generator). There may be unsoldered contacts or so-called “dry” soldering. It is possible that the terminals are not tightened or the rectifier unit is broken.
What to do?
Most likely, you have already guessed that the first thing you need to do is check all contacts and clean all detected oxides. If after a short period of time the problem repeats, then it is necessary to check the tightness of the battery; if a visual inspection yields results in the form of detected cracks and leaks, then the battery will have to be changed.
The generator on the VAZ gets hot, how to fix the problem
The generator gets very hot, every 10 owners of VAZ and Lada cars face this problem. In fact, not only the domestic auto industry suffers from this disease, including many foreign cars that quite often have problems with generator overheating.
If the generator in your car heats up, then you should not put the problem on hold, as it is quite serious. It is better to immediately contact specialists for diagnosis and subsequent repairs.
Why does the terminal get hot?
Quite large currents flow from the battery to the starter, and then from the generator back to the battery. Just think - starting currents, in winter, can reach up to 600A. If you install a thin wire, it will simply not be able to cope with such a load and will melt before your eyes. This is why the wires are so thick and solid, all because they are designed to carry high loads.
Let's watch a short video.
There are not many reasons and they are all banal:
- The problem is in the terminal itself . There is poor contact between the wire and the fastener, sometimes it comes straight from the factory, a manufacturing defect (for example, the hole in the terminal is 10 mm, and the wire is 8 mm).
- It happens over time that water can get into this place or oxides can form. The bottom line is that wires and fasteners are often made of different metals, the potential difference sooner or later leads to oxidation of the contact point and the current conductivity drops significantly.
- Oxides between the terminal and the current terminal. This also happens, but rarely, if the contact is bad, then the current must pass through a very narrow point of contact. Warming up can come from here.
- The wire . Sometimes the wire itself suffers, say, from an accidental break in the middle that is not visible to the eye. That is, several threads were broken, and the load that he could bear decreased.
- Poor contact with body . Often it is the negative cable and after the terminal that get hot. This is because it is bolted to the car body, and then both the starter and the generator are “powered” from the body. On modern foreign cars, the negative cable is quite short (on some cars it is attached to the engine block). So, the cable will heat up, but you will mistakenly think that it is the terminal (although with such a malfunction, the braiding of the wire itself will most likely begin to recover).
The positive terminal can only heat up from poor contact or, again, from oxides that have formed between the mount and the current terminal.
Why does the diode bridge of the generator get hot?
Excessive heating of the generating device will certainly lead to further problems. Heating occurs for various reasons, but most often the diodes in the unit burn out.
In general, checking the diode bridge in such cases is a must. It happens that after overhauling the generating device or replacing machine components, the car service center forgets to put gaskets on. For example, under the rectifier unit itself. Because of this, the device begins to get very hot, as it short-circuits to the case without protection (gasket).
Faulty diode bridge of the VAZ generator
It could also be this: the soldering on the diode bridge is relaxing. The reason will only be revealed by opening the GU (generator). There may be unsoldered contacts or so-called “dry” soldering. It is possible that the terminals are not tightened or the rectifier unit is broken.
Should the generator warm up?
Should the generator warm up at all?
The generator, like any other working unit of the car, must heat up and this is completely normal! The generator heats up mainly for three reasons. The first reason is that the generator is located next to the car engine; during operation, the engine heats up and the heat is transferred to the generator. The second reason is from voltage, if after starting the internal combustion engine you turn on the fog lights, glass blowing, high beams, etc. the generator will be loaded and it will start to heat up. The third reason is a malfunction of the generator, which is exactly what we will talk about a little later.
As you can see, in most cases it is considered quite normal for a car generator to heat up. Since its normal operating temperature is approximately 60 - 70 degrees. If the generator gets very hot, then I recommend that you immediately contact a service station.