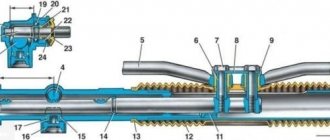
Camshaft VAZ 2107
The camshaft is the main element of the gas distribution mechanism of a car engine. This is an all-metal part, made in the form of a cylinder with support journals and cams placed on it.
The camshaft contains cams and journals
Purpose
The timing shaft is used to control the processes of opening and closing valves in the combustion chambers of the engine. In other words, it synchronizes the operating strokes of the power unit, promptly admitting the fuel-air mixture into the combustion chambers and releasing exhaust gases from them. The camshaft of the “seven” is driven by the rotation of its star (gear), connected through a chain to the crankshaft gear.
Where is it located?
Depending on the design of the engine, the timing shaft may have a different location: upper and lower. With its lower location, it is installed directly in the cylinder block, and with its upper location, it is installed in the cylinder head. For "sevens" the camshaft is located in the upper part of the cylinder head. This arrangement, first of all, makes it easily accessible for repair or replacement, as well as for adjusting valve clearances. In order to get to the timing shaft, just remove the valve cover.
Operating principle
As mentioned, the camshaft is driven by the crankshaft gear. At the same time, its rotation speed, due to the different sizes of the drive gears, is reduced exactly by half. The full operating cycle of the engine occurs in two revolutions of the crankshaft, but the timing shaft makes only one revolution, during which it manages to let the fuel-air mixture into the cylinders one by one and release the exhaust gases.
The opening (closing) of the corresponding valves is ensured by the action of the cams on the valve tappets. It looks something like this. When the shaft rotates, the cam with its protruding side presses the pusher, which transmits force to the spring-loaded valve. The latter opens a window for the intake of the combustible mixture (exhaust of gases). As the cam rotates further, the valve closes under the action of a spring.
The valves open when the protruding parts of the cams press on them
Characteristics of the VAZ 2107 camshaft
The operation of the VAZ 2107 timing shaft is determined by three main parameters:
- phase width - 232o;
- intake valve lag - 40°;
- exhaust valve advance - 42o.
The number of cams on the camshaft corresponds to the number of intake and exhaust valves. The "seven" has eight of them - two for each of the four cylinders.
Find out more about the operation of the timing belt: https://bumper.guru/klassicheskie-modeli-vaz/grm/grm-2107/metki-grm-vaz-2107-inzhektor.html
VAZ 2106 – timing chain
Upper marks: one mark in the form of a hole is applied to the camshaft sprocket from the inside, the second mark is a boss in the form of a protrusion at the end of the camshaft bed. To perform this operation, the valve cover must be removed.
Bottom marks: three marks are cast on the front engine cover - one long and two short, and on the crankshaft pulley there is a molded boss on the inside (you can easily feel it with your hand) and a mark on the end of the pulley. The long mark corresponds to the top dead center, and the two short marks are the ignition timing marks.
The first short mark (the middle of the three) corresponds to an ignition advance of 7.5 degrees, this is actually the factory tolerance for installing the ignition when using AI 92-95 gasoline. The second short mark corresponds to an ignition advance of 10 degrees.
Is it possible to increase the power of a VAZ 2107 engine by installing a different camshaft?
Probably, every owner of the “Seven” wants the engine of his car to work not only without interruptions, but also with maximum efficiency. Therefore, some craftsmen are trying to tune power units using various methods. One of these methods is to install a different, more “advanced” camshaft.
The essence of tuning
Theoretically, it is possible to increase the power performance of a power unit by increasing the phase width and lift height of the intake valve. The first indicator determines the period of time during which the intake valve will be open, and is expressed in the angle of rotation of the timing shaft. For the “seven” it is 232o. The lift height of the intake valve determines the area of the hole through which the fuel-air mixture will be supplied to the combustion chamber. For VAZ 2107 it is 9.5 mm. Thus, again, in theory, as these indicators increase, we get a larger volume of combustible mixture in the cylinders, which can really have a positive effect on the power of the power unit.
The phase width and lift height of the intake valve can be increased by changing the configuration of the corresponding cams of the gas distribution shaft. Since such work cannot be done in a garage, for such tuning it is better to use a finished part from another car.
Camshaft from Niva
There is only one car whose camshaft is suitable for the “seven”. This is a VAZ 21213 Niva. Its timing shaft has a phase width of 283°, and the intake valve lift is 10.7 mm. Will installing such a part on a VAZ 2107 engine give anything in reality? Practice shows that yes, there is a slight improvement in the operation of the power unit. The power increase is approximately 2 liters. s., but only at low revs. Yes, the “seven” responds a little sharper to pressing the accelerator pedal at the start, but once it gains speed, its power becomes the same.
Sports camshafts
In addition to the timing shaft from Niva, the VAZ 2107 can also be equipped with one of the shafts made specifically for “sports” tuning of power units. Such parts are produced by a number of domestic enterprises. Their cost ranges from 4,000–10,000 rubles. Let's look at the characteristics of such camshafts.
Table: main characteristics of “sports” timing shafts for VAZ 2101–2107
| Name | Phase width, 0 | Valve lift height, mm |
| "Estonian" | 256 | 10,5 |
| "Estonian +" | 289 | 11,2 |
| "Estonian-M" | 256 | 11,33 |
| Shrik-1 | 296 | 11,8 |
| "Shrik-3" | 304 | 12,1 |
Camshaft knock: what to do
If the camshaft begins to knock on the car, the driver should be prepared to incur significant costs. At the same time, we are not talking about replacing the camshaft, since faulty hydraulic compensators or bearings can also cause detonation. Based on this, we can conclude that if there is a suspicion of knocking in the camshaft, you should send the car for diagnostics as soon as possible. It is quite possible that this will reveal not only problems in the units responsible for synchronizing the engine clocks, but also in other elements.
READ After Replacing Timing Belt, Valves Knock Appeared
It is important to note that by delaying diagnosis, the driver risks increasing the cost of repairs. If the hydraulic jacks begin to fail, the camshaft may not function properly. Based on this, the sooner the diagnosis is made and the cause of camshaft detonation is determined, the less likely it is to fail.
Cars that are not equipped with hydraulic lifters can drive more than 50,000 kilometers with camshaft shock, but after that you may need a complete engine replacement or overhaul.
Malfunctions of the VAZ 2107 camshaft, their symptoms and causes
Considering that the timing shaft is subject to constant dynamic and temperature loads, it cannot last forever. It is difficult even for a specialist to determine that this particular unit has failed without detailed diagnostics and troubleshooting. There may be only two signs of its malfunction: a decrease in power and a quiet knocking sound, which manifests itself mainly under load.
The main camshaft faults include:
- wear of the working bodies of the cams;
- wear of the surfaces of the bearing journals;
- deformation of the entire part;
- shaft fracture.
More about timing chain repair: https://bumper.guru/klassicheskie-modeli-vaz/grm/grm-2107/kak-natyanut-tsep-na-vaz-2107.html
Wear of cams and journals
Wear is a natural occurrence for a constantly rotating part, but in some cases it can be excessive and premature. This leads to:
- insufficient oil pressure in the system, as a result of which lubricant does not flow to loaded areas or is supplied in smaller quantities;
- low-quality motor oil or one that does not meet established requirements;
- defect in the production of the shaft or its “bed”.
If the cams wear out, the engine power is noticeably reduced, since they, being worn out, cannot provide either the appropriate phase width or the required lift of the intake valve.
When the cams wear out, engine power drops
Deformation
Camshaft deformation occurs as a result of severe overheating caused by malfunctions of the lubrication or cooling systems. At the initial stage, this malfunction may manifest itself in the form of a characteristic knocking sound. If you suspect such a breakdown, further operation of the car is not recommended, as it can damage the entire gas distribution mechanism of the engine.
Deformation occurs due to malfunctions in the lubrication and cooling systems
Fracture
A camshaft fracture may be a consequence of its deformation, as well as poor timing. In the event of this malfunction, engine operation stops. In parallel with this problem, others arise: destruction of the shaft “bed”, bending of valves, guides, damage to parts of the piston group.
A shaft fracture may be a consequence of deformation
How to understand that the camshaft needs to be changed?
You can determine a camshaft malfunction without opening the hood by two signs:
The main reason for malfunctions in the camshaft is the appearance of gaps. They appear between the shaft bearing journals and the bed bearings on which the camshaft rests. The cracks are formed due to the fact that parts of the camshaft are worn away. Gaps cause the shaft to move in the vertical or horizontal axis. If the shaft play is 1 mm, then this affects the operation of the engine. Reasons for gaps:
The camshaft also needs to be changed if the oil channels in it are clogged. Before changing the part, look for any play, fracture, deformation or scuffing of the shaft.
Troubleshooting the VAZ 2107 timing shaft
When the camshaft is removed from the “bed”, it is necessary to assess its condition. First this is done visually. The camshaft must be replaced if its working surfaces (cams and bearing journals) have:
- scratches;
- bullies;
- cut wear (for cams);
- enveloping a layer of aluminum from the “bed” (for support necks).
In addition, the camshaft must be replaced if even the slightest traces of deformation are found.
The degree of wear of the support journals and the supports themselves is determined using a micrometer and caliper. The table below shows the permissible diameters of the journals and working surfaces of the supports.
Defect detection is carried out using a micrometer and calipers
Table: permissible diameters of the camshaft journals and its “bed” supports for VZ 2107
| Serial number of the neck (support), starting from the front | Allowable dimensions, mm | |
| Minimum | Maximum | |
| Support journals | ||
| 1 | 45,91 | 45,93 |
| 2 | 45,61 | 45,63 |
| 3 | 45,31 | 45,33 |
| 4 | 45,01 | 45,03 |
| 5 | 43,41 | 43,43 |
| Supports | ||
| 1 | 46,00 | 46,02 |
| 2 | 45,70 | 45,72 |
| 3 | 45,40 | 45,42 |
| 4 | 45,10 | 45,12 |
| 5 | 43,50 | 43,52 |
If during the inspection it is determined that the dimensions of the working surfaces of the parts do not correspond to those given, the camshaft or “bed” must be replaced.
Installing a new camshaft
In order to install a new timing shaft, you will need the same tools as to dismantle it. The installation procedure is as follows:
- Be sure to lubricate the surfaces of the cams, bearing journals and bearings with engine oil.
- We install the camshaft in the “bed”.
- Using a 10 mm wrench, tighten the bolts of the thrust flange.
- We check how the shaft rotates. It should turn easily around its axis.
- We set the shaft to such a position that its pin would coincide with the hole on the fixing flange.
- We install the bed on the studs, screw on the nuts, and tighten them. It is important to follow the established procedure. The tightening torque is in the range of 18.3–22.6 Nm.
The nuts are tightened using a torque wrench with a torque of 18.3–22.6 Nm - We do not install the valve cover and camshaft sprocket in place, since it will still be necessary to set the valve timing.
Setting ignition timing (valve timing) by marks
After the repair work has been carried out, it is necessary to set the correct ignition timing. To do this you need to do the following:
- Install the camshaft sprocket with the chain, secure it with a bolt without tightening it.
- Install the chain tensioner.
- Place the chain over the crankshaft, accessory shaft and camshaft gears.
- Using a 36mm wrench placed on the crankshaft pulley nut, rotate the crankshaft until the mark on the pulley aligns with the mark on the engine cover.
Labels must match - Determine the position of the camshaft sprocket in relation to the “bed”. The mark on the star should also line up with the protrusion.
If the marks do not match, you need to shift the sprocket relative to the chain - If the marks do not match, unscrew the camshaft sprocket bolt and remove it together with the chain.
- Remove the chain and turn the sprocket to the left or right (depending on where the mark is shifted) by one tooth. Place the chain on the sprocket and install it on the camshaft, securing it with a bolt.
- Check the position of the marks.
- If necessary, repeat shifting the star by one tooth until the marks coincide.
- Upon completion of work, secure the star with a bolt and the bolt with a washer.
- Install the valve cover.
Secure it with nuts. Tighten the nuts in the order shown in the photo. Tightening torque: 5.1–8.2 Nm. The nuts must be tightened with a torque wrench to a torque of 5.1–8.2 Nm - Carry out further engine assembly.
Do it yourself: Replacing the camshaft, rockers and caps of the VAZ-2107
Hello everyone, I decided to replace the camshaft with rockers, and at the same time the valve stem seals. The previous owner already changed the factory camshaft and rocker at 120 thousand km, now the mileage is approaching 230 thousand km, so I think it’s time, especially since the last adjustment of the valves did not give any results - the chirping sound did not change in any way, so there were suspicions about wear cams with rockers. The oil is still leaking, and then suspicions fell on the valve stem seals, since there were characteristic signs of their wear - when starting up after an overnight stop, there is a lot of smoke from the exhaust pipe in the first seconds.
Well, and the carving of candles in soot.
Also, when inspecting the cylinders with an inspection camera, wet smudges were discovered on the exhaust valves.
So, I purchased a camshaft assembly, a set of rockers with new-style adjusting bolts, Reserve oil seals (they seem to be praising them), a couple of crackers and springs, just in case. Among the tools, I bought a desiccant, a mandrel for stuffing oil seals, I didn’t buy a puller (the toad strangled me), instead I bought narrow-nose pliers.
We remove the valve cover, set the TDC marks on the 4th cylinder, remove the camshaft sprocket with the chain so that it does not jump, tie it with a rope with the star, since you will then have to turn the crankshaft again.
Then I removed the camshaft, disassembled it and wiped off the oil to get a better look.